Blast Furnace
Blast Furnace
Was ist ein Blast Furnace?
Ein Blast Furnace, auf Deutsch "Hochofen", spielt eine zentrale Rolle in der Stahlindustrie. Er wird zum Schmelzen bestimmter Erze verwendet, um Metall, insbesondere Roheisen, zu extrahieren. Diese großvolumigen, turmartigen Öfen sind ein wichtiger Bestandteil im Stahlhandel, vor allem in der Roheisenproduktion für die Stahlerzeugung.
Die Funktionsweise eines Blast Furnace
Im Blast Furnace werden Metallerze, in der Regel Eisenoxid (Eisenerz), kohlenstoffhaltige Materialien (Koks) und Kalkstein zusammengemischt und erhitzt. Durch die hohe Temperatur - oft über 2000 Grad Celsius - spaltet sich das Erz: Der Eisenanteil sinkt zum Boden des Ofens und das Abfallprodukt, die sogenannte Schlacke, wird entfernt. Der so gewonnene flüssige Eisenträger ist das Roheisen, der wichtigste Ausgangsstoff in der Stahlproduktion.
Blast Furnace in der Stahlproduktion und im Stahlhandel
Der Blast Furnace ist eine unverzichtbare Komponente im Stahlhandel. Ohne die Hochofen-Technologie wäre eine großtechnische Herstellung von Stahl kaum vorstellbar. Die von Blast Furnaces produzierte Roheisenmenge ist ein wichtiger Indikator für die gesamte Leistung der Stahlindustrie. Daher sind Entwicklungen und Verbesserungen der Hochofen-Technologie von großer Bedeutung für Stahlproduktion und Stahlhandel.
Zukunft der Blast Furnace
Obwohl moderne Technologien wie die Direktreduktion von Eisen (DRI) erfolgsversprechende Alternativen zum Blast Furnace darstellen, bleibt dieser doch ein zentraler Bestandteil in der Stahlindustrie. Die kontinuierliche Optimierung von Hochöfen zielt insbesondere auf effizientere Prozesse und einen reduzierten CO2-Ausstoß ab. Dies hilft nicht nur dabei, Kosten zu sparen, sondern auch, den umweltbelastenden Einfluss der Stahlherstellung zu mindern.
Blog Posts with the term: Blast Furnace

Steel making is a sophisticated process that turns iron ore into steel, involving methods like the Blast Furnace and Electric Arc Furnace to produce various grades of steel. The industry emphasizes sustainability by using additives and recycled materials while ensuring...

The article provides an overview of the steel making process, detailing how raw materials like iron ore, coke, and limestone are transformed into versatile and durable steel through a complex series of steps depicted in a flow diagram. It discusses...

The article provides an overview of the two main steelmaking routes: blast furnace (BF) and electric arc furnace (EAF), detailing their processes, economic considerations, environmental impacts, and technological advancements. It compares BF's large-scale production with high carbon emissions to EAF's...
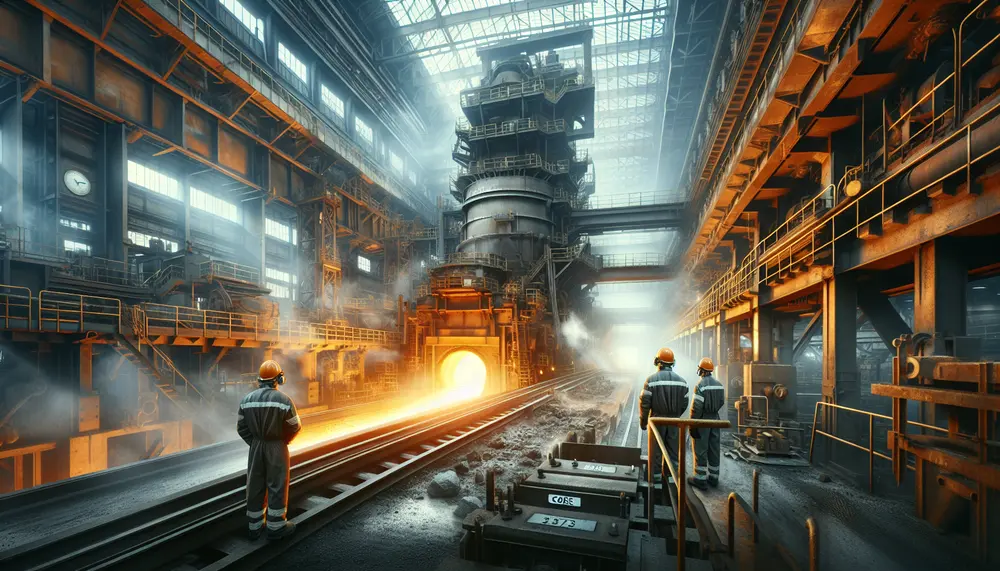

Coke is crucial in steel production, providing heat and chemical reactions for smelting iron ore while also structuring the blast furnace. However, its use emits pollutants and CO2, contributing to environmental concerns....
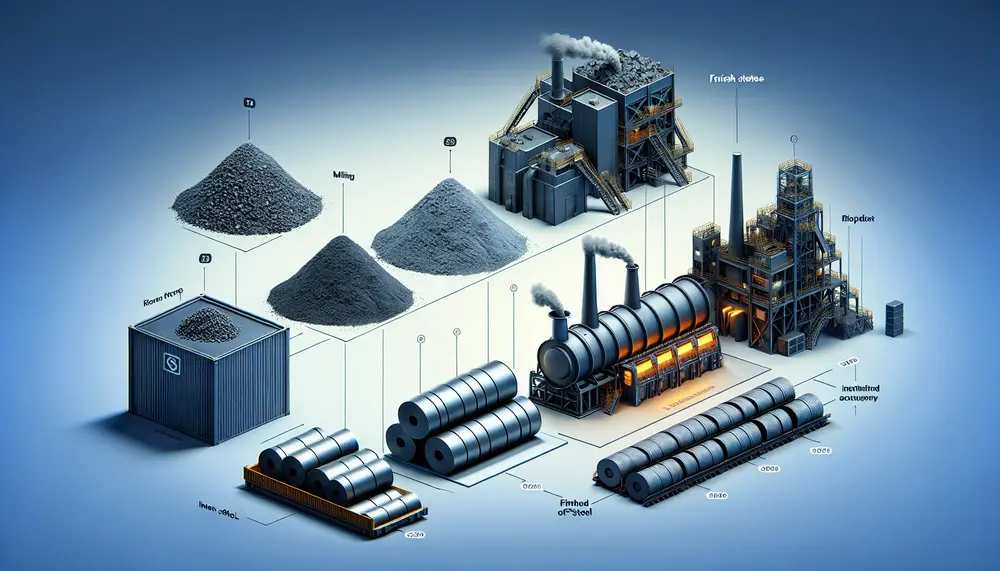
The steelmaking value chain is a complex process that transforms raw materials like iron ore, coking coal, and limestone into high-quality steel through strategic steps involving technological innovation to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Understanding this value chain helps...

Mexico's steel industry has grown significantly due to rich resources, strategic location, skilled workforce, and modern technology. Challenges include high energy costs, competition from lower-cost countries, price fluctuations, and environmental concerns....
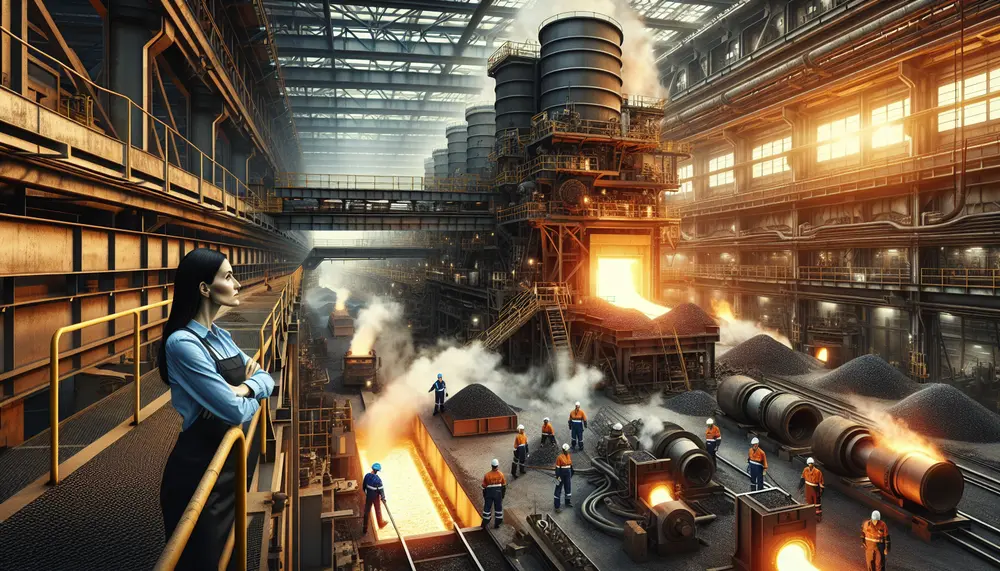

The article "Introduction to Steelmaking from Pig Iron" explores the historical and modern processes of transforming pig iron into steel, including methods like the Bessemer Process, Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS), and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). It highlights the importance of...

Oman's steel production has seen significant growth, contributing to the nation's GDP and infrastructure development. Strategic expansions have increased capacity to over 2.4 million tons, with key players like Muscat Steel Industries Co. LLC driving this dynamic sector forward through...

The steel industry in the Netherlands is integral to its economy, known for innovation and sustainability, with a focus on high-grade production used across various sectors. The Dutch sector's evolution has been shaped by historical shifts and strategic investments like...

Steel, an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, is a crucial material in modern construction and manufacturing due to its strength, flexibility, and durability. The process of making steel involves extracting iron ore, purifying it through beneficiation processes, smelting...
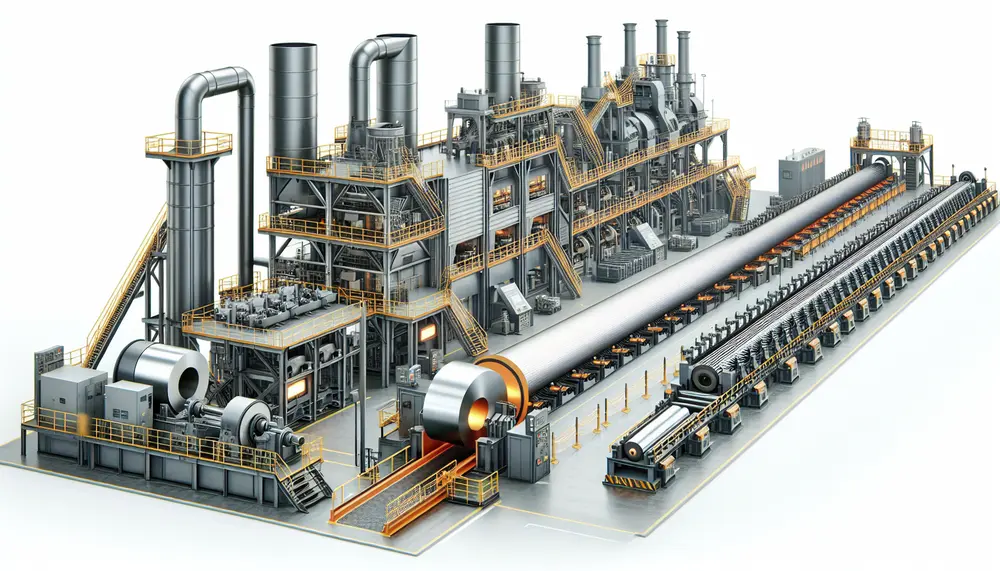
Steel manufacturing is a complex process that transforms iron ore into steel, involving precise heating and mixing to create different grades for various applications. The journey includes primary methods like Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS) and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), followed...

Steel's origins trace back to meteoric iron and evolved with human discovery of smelting around 2500 BCE, leading from the Bronze Age into the Iron Age. The Bessemer Process in the mid-19th century revolutionized steel production, enabling mass production and...

Steel production in the United States varies by state, reflecting unique resources, workforce skills, and industrial strategies; key states like Indiana, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Ohio lead due to factors such as natural resource availability and technological innovation. Mini-mills have revolutionized...

The steelmaking industry is increasingly using natural gas to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Natural gas serves as a reducing agent in Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) processes, partially replaces coke in blast furnaces, fuels various types of industrial furnaces,...

