Liquid steel
Liquid steel
Was ist Liquid Steel?
Liquid steel – Der Prozess der Stahlherstellung ist komplex und besteht aus einer Reihe von Schritten, die aufeinander aufbauen. Eine wichtige Phase in diesem Prozess ist die Herstellung von flüssigem Stahl, auch "liquid steel" genannt. Aber was genau ist unter diesem Begriff zu verstehen? Kurz gesagt handelt es sich dabei um Stahl in flüssiger Form, der noch eine hohe Temperatur aufweist und sich noch im Schmelzzustand befindet.
Wie entsteht Liquid Steel?
Die Produktion von liquid steel erfolgt in spezialisierten Hochöfen, die auf Temperaturen von bis zu 1700 Grad Celsius erhitzt werden können. Diese enorme Hitze ist notwendig, um das Stahlrohmaterial - meist Eisenerz, Kohle und Kalkstein - aufzuschmelzen. Dabei entsteht zunächst Roheisen, das allerdings noch viele Unreinheiten enthält. Durch ein Verfahren namens Frischen wird das Roheisen von diesen Verunreinigungen befreit und in seine flüssige Form überführt.
Liquid Steel - im Handel und bei der Weiterverarbeitung
Beim Transport und Handel wird der liquid steel in sogenannten Torpedowagen transportiert. Diese sind so konstruiert, dass sie die extreme Hitze und das Gewicht des flüssigen Stahls tragen können. Nachdem der liquid steel an seinen Bestimmungsort gebracht wurde, wird er durch verschiedene Gießverfahren in die gewünschte Form gebracht. Dies kann sowohl in Form von Blechen, Rohren oder anderen spezialisierten Produkten geschehen.
Total Accessible Market für Liquid Steel
Der globale Markt für liquid steel ist umfangreich und beinhaltet zahlreiche Arten von Produzenten und Konsumenten. Große Mengen des flüssigen Stahls werden zur Herstellung verschiedenster Güter verwendet, vom simplen Haushaltsgerät über den Automobilbau bis hin zu riesigen Brückenkonstruktionen. Der wachsende Bedarf an robusten und langlebigen Materialien, vor dem Hintergrund der steigenden urbanen Infrastruktur weltweit, hält die Nachfrage nach liquid steel hoch und nimmt kontinuierlich zu.
Blog Posts with the term: Liquid steel

Steel making is a sophisticated process that turns iron ore into steel, involving methods like the Blast Furnace and Electric Arc Furnace to produce various grades of steel. The industry emphasizes sustainability by using additives and recycled materials while ensuring...

The Bessemer process, developed by Henry Bessemer in the 1850s, revolutionized steel production by efficiently removing impurities from molten pig iron using blown air and enabling mass production. This innovation significantly reduced costs and time for steel manufacturing, facilitating industrial...
Steel manufacturing is a complex process that transforms iron ore into steel, involving precise heating and mixing to create different grades for various applications. The journey includes primary methods like Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS) and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), followed...

Steel's origins trace back to meteoric iron and evolved with human discovery of smelting around 2500 BCE, leading from the Bronze Age into the Iron Age. The Bessemer Process in the mid-19th century revolutionized steel production, enabling mass production and...

The steel making process, which starts with the extraction of iron ore and involves several steps to create different types of steel, is transitioning towards more sustainable methods like the Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) method. The BOF method turns raw...

The blast furnace steel making process involves transforming raw materials into molten iron, which is then processed to produce steel. Key components include coke, iron ore and limestone; the former provides heat while the latter two undergo chemical reactions in...
The steel making degassing process is essential for producing high-quality steel by removing dissolved gases like hydrogen, nitrogen, and carbon monoxide to prevent material defects. Vacuum degassing enhances the mechanical properties of steel, crucial for applications in construction and manufacturing,...
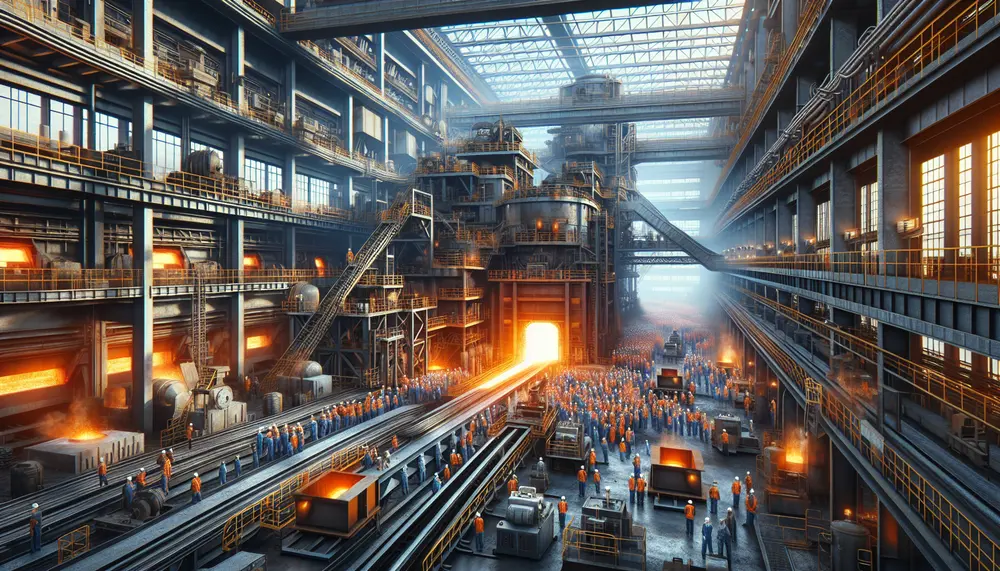

The article provides a detailed overview of the steelmaking process, starting from raw material extraction to final product creation. It emphasizes the importance of understanding each stage and the key materials involved—iron ore, coal, limestone, and scrap metal—to produce high-quality...

The steelmaking process involves complex chemical reactions to transform iron ore into steel, an alloy primarily made of iron and carbon. The Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS) method is the most common way to produce steel, where a high-purity stream of...
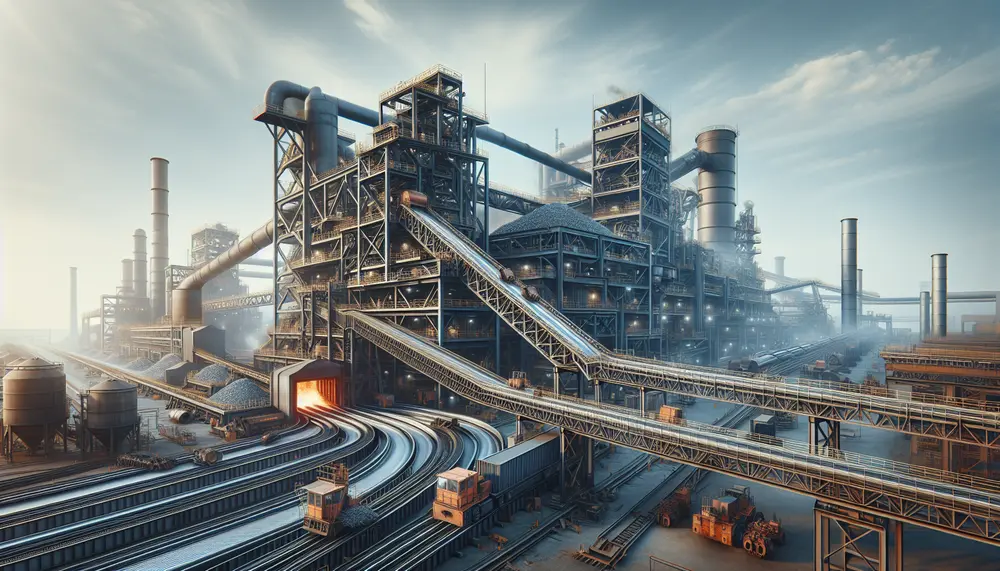

Steel manufacturing from scrap is a sustainable process that reduces environmental impact and conserves resources. It involves collection, separation, melting in an electric arc furnace, refining to remove impurities, adding alloy elements, and casting into new products; recycling steel offers...
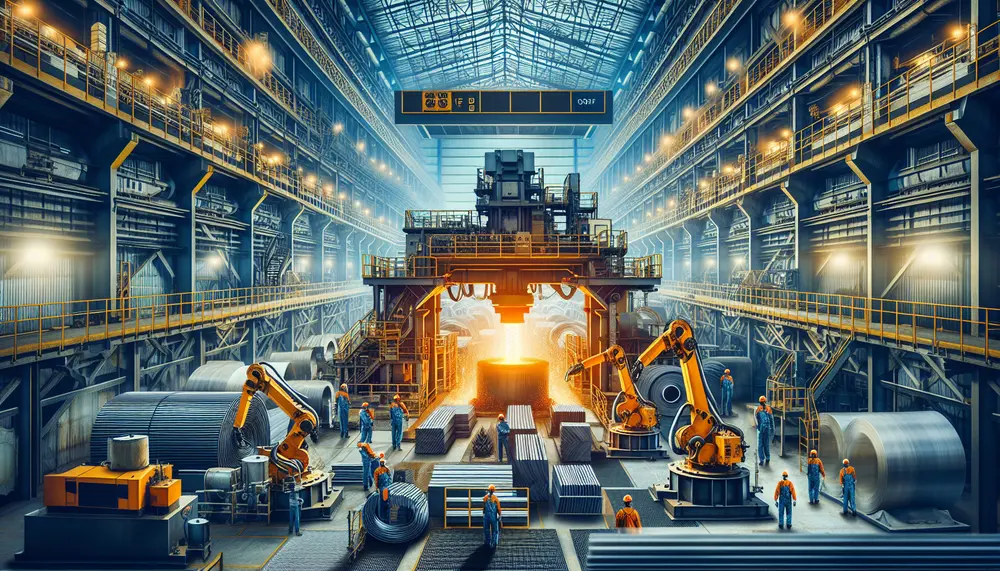

RH technology, initially developed for hydrogen removal in steel making, now plays a crucial role in secondary refining and purification to ensure high-quality steel production. Key advancements like oxygen lances, powder injection systems, the RH-TOP system, and modern vacuum pumps...

A steel product is an item predominantly made of steel, known for its durability and versatility across industries, with a wide range of forms and applications. Understanding these products involves knowledge of the production process from raw materials to finished...
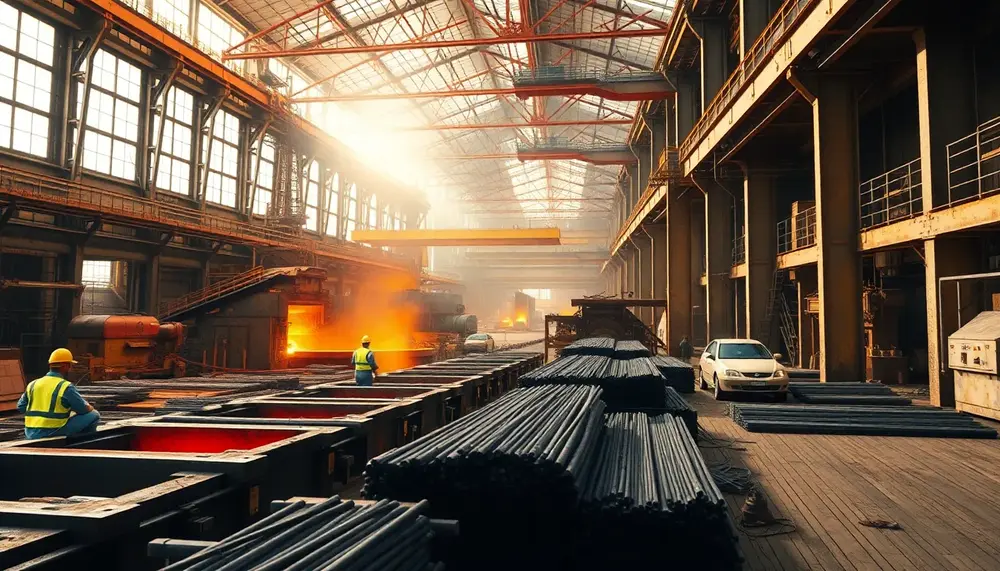

Rebar, a steel reinforcement bar used in concrete and masonry structures, enhances tensile strength to prevent cracking and structural failure; its various types cater to specific environmental needs while ensuring durability, safety, and cost-effectiveness in construction projects....
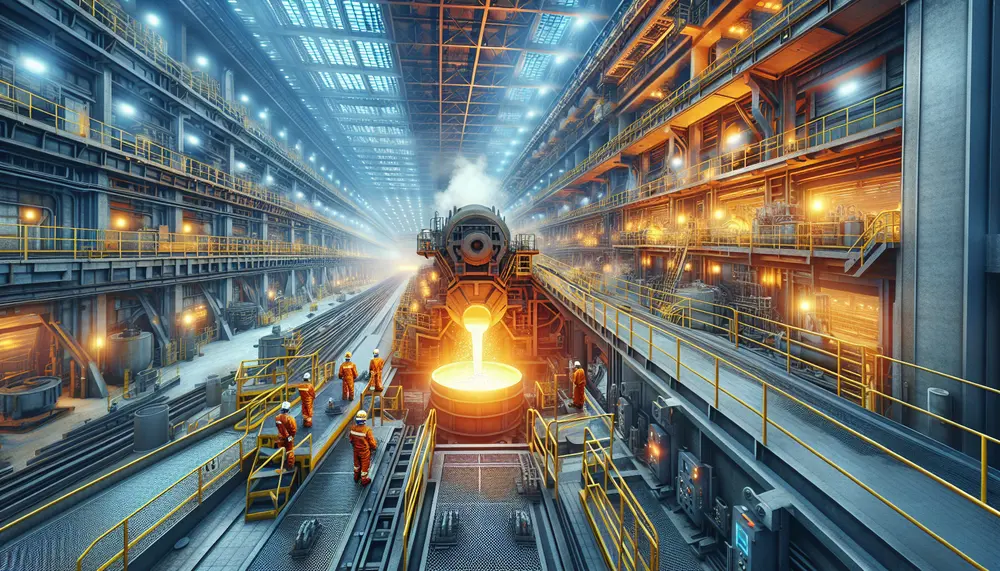

The Ladle Metallurgy Furnace (LMF) is a crucial advancement in modern steel production, allowing for precise control over the chemical composition and temperature of molten steel to produce high-quality products. This technology involves transferring liquid steel into a specialized furnace...

