Productivity
Productivity
Was ist 'Productivity' in der Stahlproduktion und im Stahlhandel?
Der Begriff 'Productivity', auf Deutsch 'Produktivität', spielt eine fundamentale Rolle in der Welt der Stahlproduktion und des Stahlhandels. Es ist ein Maß dafür, wie effizient Produktionsfaktoren eingesetzt werden, um Produkte herzustellen. Es gibt Produktivität auf Unternehmen, industriellem und nationalem Niveau.
Wie misst man sie in der Stahlindustrie?
In der Stahlindustrie ist die Produktivität oft ein Verhältnis von Output zu Input. Der Output umfasst die produzierten Mengen an Stahl, während der Input Faktoren wie Arbeitszeit, Material, Energie und Kapital beinhaltet. Eine hohe Produktivität bedeutet also, dass die Produktionsmittel effizient genutzt werden und somit größere Mengen an Stahl mit weniger Ressourcen erzeugt werden können.
Warum ist 'Productivity' wichtig?
Die Produktivität hat großen Einfluss auf den Erfolg eines Stahlunternehmens. Ein hoher Grad an Produktivität bedeutet einen effizienten Einsatz von Ressourcen. Dadurch können Kosten gesenkt und Wettbewerbsvorteile erzielt werden. Zudem hat eine verbesserte Produktivität oftmals auch positive Auswirkungen auf Umwelt- und Klimaschutzziele, da eine effizientere Produktion weniger Ressourcen verbraucht und weniger Emissionen produziert.
Wie kann die 'Productivity' verbessert werden?
Es gibt verschiedene Wege, die Produktivität im Bereich der Stahlproduktion zu steigern. Beispielsweise können technologische Neuerungen dazu beitragen, Prozesse zu optimieren und so den Output zu steigern oder den Input zu verringern. Darüber hinaus können Weiterbildungen und Schulungen der Mitarbeiter dabei helfen, Fähigkeiten zu verbessern und Prozesseffizienz zu steigern. Auch organisatorische Änderungen, wie zum Beispiel die Verbesserung der Arbeitsabläufe, können die Produktivität erhöhen.
Blog Posts with the term: Productivity

Steel making is a sophisticated process that turns iron ore into steel, involving methods like the Blast Furnace and Electric Arc Furnace to produce various grades of steel. The industry emphasizes sustainability by using additives and recycled materials while ensuring...

The article provides an overview of the two main steelmaking routes: blast furnace (BF) and electric arc furnace (EAF), detailing their processes, economic considerations, environmental impacts, and technological advancements. It compares BF's large-scale production with high carbon emissions to EAF's...

Steel production is vital in Anno 1800, requiring a strategic layout of mines and factories to efficiently transform iron ore into steel beams and weapons. Optimizing the placement and synchronization of these facilities ensures a smooth industrial operation essential for...

Nigeria's steel production industry is crucial for its industrial development, with potential to become a major producer due to iron ore deposits. However, the sector faces challenges such as small-scale operations and requires strategic solutions for sustainable growth. The evolution...

Coke is crucial in steel production, providing heat and chemical reactions for smelting iron ore while also structuring the blast furnace. However, its use emits pollutants and CO2, contributing to environmental concerns....

The steel industry is essential but poses significant risks to workers, including physical dangers from heavy machinery and extreme heat, chemical hazards from toxic substances, burn threats due to high temperatures in furnaces, and noise pollution leading to potential hearing...

The African steel industry is growing and diverse, with varying levels of resource availability and technological sophistication across countries. It plays a crucial economic role by stimulating growth in other sectors, creating jobs, contributing to GDP, reducing import dependency, and...

Steel production in France has grown due to technological advancements, increased demand, and strategic investments despite challenges like environmental regulations and market volatility. The industry's history shows a pattern of expansion post-WWII, peak production in the 1970s, followed by decline...
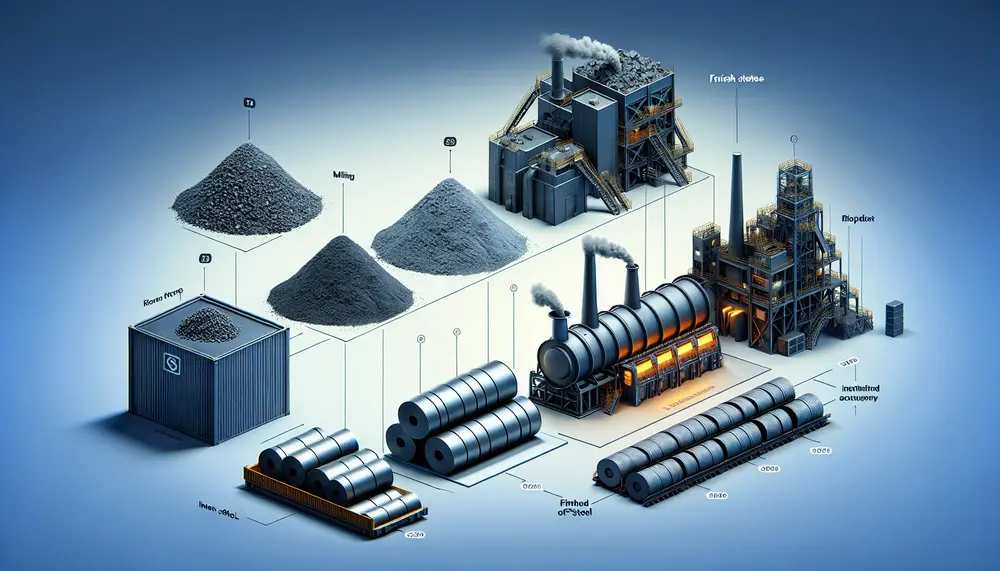
The steelmaking value chain is a complex process that transforms raw materials like iron ore, coking coal, and limestone into high-quality steel through strategic steps involving technological innovation to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Understanding this value chain helps...

Mexico's steel industry has grown significantly due to rich resources, strategic location, skilled workforce, and modern technology. Challenges include high energy costs, competition from lower-cost countries, price fluctuations, and environmental concerns....

Steel, an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, is a crucial material in modern construction and manufacturing due to its strength, flexibility, and durability. The process of making steel involves extracting iron ore, purifying it through beneficiation processes, smelting...

Steel's origins trace back to meteoric iron and evolved with human discovery of smelting around 2500 BCE, leading from the Bronze Age into the Iron Age. The Bessemer Process in the mid-19th century revolutionized steel production, enabling mass production and...

Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are crucial for the steel industry, guiding operational improvements and aligning business objectives with market demands. They include metrics like energy consumption rates and CO2 emissions, which help companies increase profitability while adhering to sustainability goals....

The steelmaking industry is increasingly using natural gas to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Natural gas serves as a reducing agent in Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) processes, partially replaces coke in blast furnaces, fuels various types of industrial furnaces,...

