Carbon Content
Carbon Content
Was ist der Kohlenstoffgehalt oder 'Carbon Content'?
Der Carbon Content oder Kohlenstoffgehalt ist ein essenzielles Element in der Stahlproduktion und dem Stahlhandel. Er bezieht sich auf den Prozentsatz des Kohlenstoffgehalts in einer Stahllegierung. Dieser kann den Charakter des Stahls, seine Beanspruchbarkeit und seine Nutzungsmöglichkeiten stark beeinflussen.
Wirkung des Kohlenstoffgehalts auf Stahl
Der Carbon Content hat erhebliche Auswirkungen auf die Eigenschaften von Stahl. Mit einer Erhöhung des Kohlenstoffgehalts, wird Stahl in der Regel härter und stärker. Jedoch kann dies auch zu einer Verringerung der Zähigkeit und einer Erhöhung der Sprödigkeit führen. Daher ist eine genaue Abstimmung des Kohlenstoffgehalts für bestimmte Anwendungen erforderlich.
Carbon Content und Stahlqualität
Der Kohlenstoffgehalt ist auch ein wichtiger Indikator für die Qualität von Stahl. Hoher Kohlenstoffgehalt spricht oft für hochwertigen Stahl, da es die Stärke und Festigkeit erhöht. Stähle mit niedrigem Kohlenstoffgehalt sind hingegen flexibler und widerstandsfähiger gegen Brüche.
Messen und Kontrolle des Carbon Content
Messen und regulieren des Carbon Content ist ein Schlüsselelement in der Stahlproduktion. Dies wird durch verschiedene Verfahren erreicht, darunter die chemische Analyse des Stahls. Eine zuverlässige Kontrolle des Kohlenstoffgehalts ist daher entscheidend für die Herstellung hochwertiger Stahlprodukte.
Carbon Content in der Praxis
Im praktischen Gebrauch spielt der Carbon Content eine entscheidende Rolle für den Stahlhandel. Da verschiedene Arten von Stahl für unterschiedliche Anwendungen verwendet werden, haben Kunden oft spezifische Vorstellungen von dem idealen Carbon Content für ihr Projekt.
Blog Posts with the term: Carbon Content

Steel making is a sophisticated process that turns iron ore into steel, involving methods like the Blast Furnace and Electric Arc Furnace to produce various grades of steel. The industry emphasizes sustainability by using additives and recycled materials while ensuring...

Coke is crucial in steel production, providing heat and chemical reactions for smelting iron ore while also structuring the blast furnace. However, its use emits pollutants and CO2, contributing to environmental concerns....
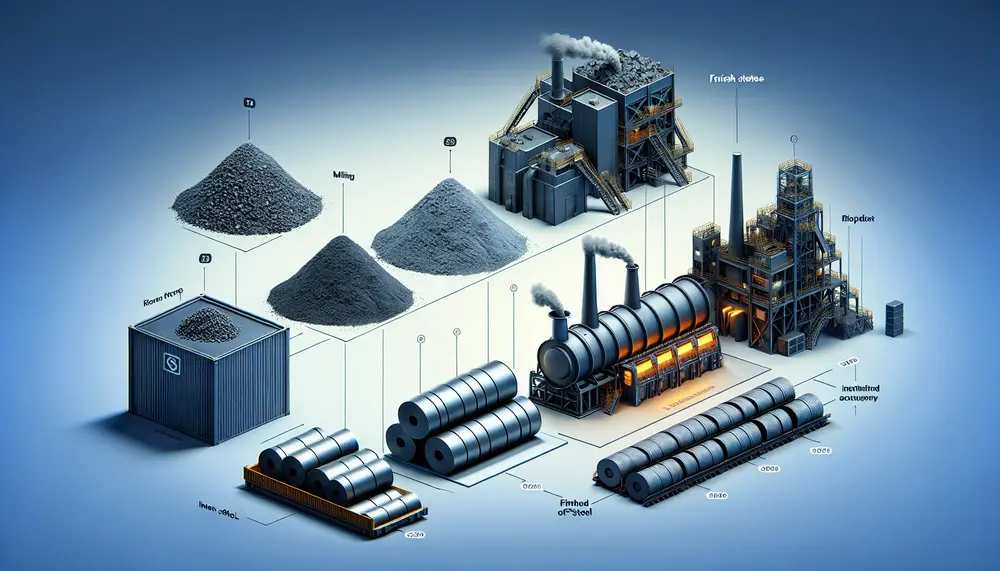
The steelmaking value chain is a complex process that transforms raw materials like iron ore, coking coal, and limestone into high-quality steel through strategic steps involving technological innovation to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Understanding this value chain helps...

Mexico's steel industry has grown significantly due to rich resources, strategic location, skilled workforce, and modern technology. Challenges include high energy costs, competition from lower-cost countries, price fluctuations, and environmental concerns....

The article "Introduction to Steelmaking from Pig Iron" explores the historical and modern processes of transforming pig iron into steel, including methods like the Bessemer Process, Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS), and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). It highlights the importance of...

Steel, an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, is a crucial material in modern construction and manufacturing due to its strength, flexibility, and durability. The process of making steel involves extracting iron ore, purifying it through beneficiation processes, smelting...

The Bessemer process, developed by Henry Bessemer in the 1850s, revolutionized steel production by efficiently removing impurities from molten pig iron using blown air and enabling mass production. This innovation significantly reduced costs and time for steel manufacturing, facilitating industrial...

Steel's origins trace back to meteoric iron and evolved with human discovery of smelting around 2500 BCE, leading from the Bronze Age into the Iron Age. The Bessemer Process in the mid-19th century revolutionized steel production, enabling mass production and...

The Argon Oxygen Decarburization (AOD) process is a secondary steel making method that refines the composition of steel by reducing carbon content, using oxygen and inert gases like argon for controlled reactions. This technology allows for high-quality alloy production with...

The article traces the evolution of steelmaking from ancient techniques to significant medieval innovations, highlighting early methods like iron carburization and bloomery processes that evolved into more efficient practices with the introduction of blast furnaces. It also covers Renaissance advancements...

Steel making involves complex chemical reactions to transform raw materials into high-quality steel, primarily through oxidation and reduction processes. Oxygen plays a crucial role in oxidizing impurities like carbon, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus, which are then removed as gases or...

The VOD (Vacuum-Oxygen-Decarburization) steelmaking process is essential for producing high-quality stainless steel with very low carbon levels, crucial for applications like medical instruments and aerospace components. While it offers advantages such as enhanced decarburization and protection of alloying elements, its...

The article explains the importance of understanding a steelmaking flow chart, which outlines each step from raw material preparation to final products, aiding in efficiency and productivity. It details key components like raw materials (iron ore, limestone, coal), primary steps...

The article explains the differences between steelmaking coal and thermal coal, highlighting their distinct uses in industry—steel production for steelmaking coal and electricity generation for thermal coal. It also discusses the importance of understanding these distinctions for businesses involved in...