Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion Resistance
Was ist Corrosion Resistance?
Der Begriff Corrosion Resistance, oder auf Deutsch Korrosionsbeständigkeit, beschreibt die Fähigkeit eines Metalls, seine strukturelle Integrität unter dem Angriff von Umwelteinflüssen zu behalten. Es ist ein grundlegender Faktor in der Steel production and steel trade, da die Haltbarkeit und Lebensdauer von Stahlprodukten stark von ihrer Korrosionsbeständigkeit abhängt.
Warum ist Corrosion Resistance in der Stahlproduktion und im Stahlhandel wichtig?
Die Bedeutung der Corrosion Resistance in der Stahlindustrie kann nicht genug betont werden. Stahl, der korrosionsbeständig ist, behält seine Stärke und seine Form über einen längeren Zeitraum. Das macht ihn wirtschaftlich wertvoll, da er weniger oft ersetzt werden muss. Das ist vor allem in Industriebereichen wichtig, in denen der Stahl rauen Umgebungen ausgesetzt ist, wie zum Beispiel in der Bauindustrie oder bei der Herstellung von Schiffen.
Wie wird Corrosion Resistance gemessen?
Die Messung der Corrosion Resistance ist ein zentraler Teil des Qualitätsmanagements in der Stahlproduktion. Sie wird typischerweise durch spezielle Tests bestimmt, bei denen Stahlproben unter kontrollierten Bedingungen aggressiven Umgebungen ausgesetzt werden. Die Rate, in der dieses Material seinen Verlust an Masse oder seine Veränderung im Aussehen verzeichnet, gibt Aufschluss darüber, wie korrosionsbeständig es ist.
Faktoren, die die Corrosion Resistance beeinflussen
Es gibt viele Faktoren, die die Corrosion Resistance von Stahl beeinflussen können. Dazu gehören die chemische Zusammensetzung des Stahls, die Verfügbarkeit von Sauerstoff und Wasser, die Umgebungstemperatur und die Anwesenheit von Verunreinigungen. Je mehr dieser Faktoren kontrolliert werden können, desto besser kann die Korrosionsbeständigkeit des Stahls garantiert werden.
Blog Posts with the term: Corrosion Resistance

Steel making is a sophisticated process that turns iron ore into steel, involving methods like the Blast Furnace and Electric Arc Furnace to produce various grades of steel. The industry emphasizes sustainability by using additives and recycled materials while ensuring...

The article provides an overview of the steel making process, detailing how raw materials like iron ore, coke, and limestone are transformed into versatile and durable steel through a complex series of steps depicted in a flow diagram. It discusses...

Steel production in France has grown due to technological advancements, increased demand, and strategic investments despite challenges like environmental regulations and market volatility. The industry's history shows a pattern of expansion post-WWII, peak production in the 1970s, followed by decline...
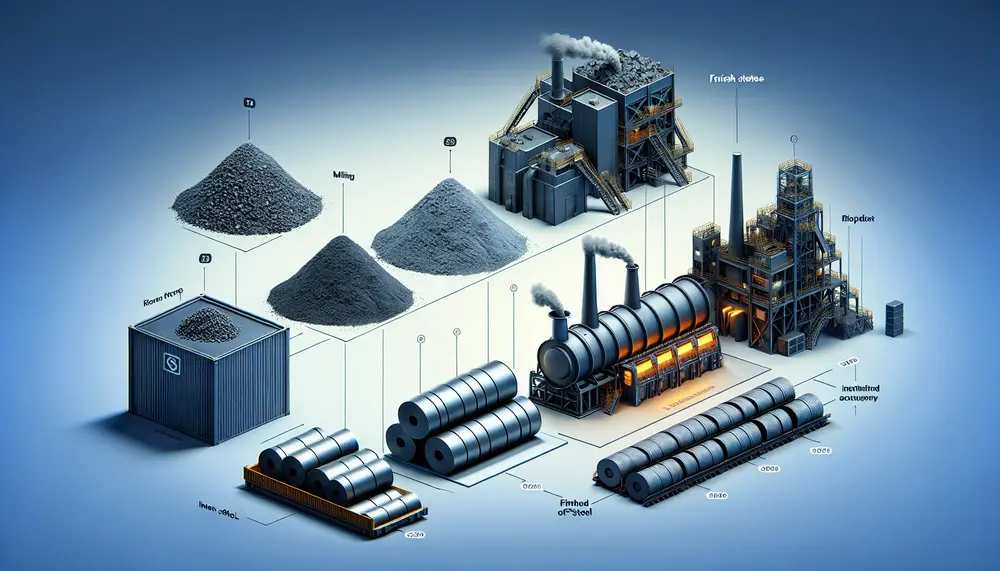
The steelmaking value chain is a complex process that transforms raw materials like iron ore, coking coal, and limestone into high-quality steel through strategic steps involving technological innovation to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Understanding this value chain helps...

The global steel production landscape is a complex network essential for various industries, influenced by factors like raw material availability and technological advancements. China leads in output with other key players being India, Japan, and the US; sustainability efforts are...

The article traces the history of steelmaking from early iron discoveries around 2,500 BCE to advanced techniques like Chinese cast iron production and Indian Wootz steel. It highlights key innovations such as smelting, forging by the Chalybes, and global influences...

Steel making involves complex chemical reactions to transform raw materials into high-quality steel, primarily through oxidation and reduction processes. Oxygen plays a crucial role in oxidizing impurities like carbon, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus, which are then removed as gases or...

The article provides an overview of steel making, detailing its historical evolution and main processes such as ironmaking, primary and secondary steelmaking, casting, and forming; it highlights the importance of methods like the basic oxygen process and electric arc furnace...

The VOD (Vacuum-Oxygen-Decarburization) steelmaking process is essential for producing high-quality stainless steel with very low carbon levels, crucial for applications like medical instruments and aerospace components. While it offers advantages such as enhanced decarburization and protection of alloying elements, its...

The article "Introduction to Ancient Steel Making" explores the historical context, key techniques, and materials used in ancient steel production across various civilizations. It highlights how early methods influenced modern steel making and underscores the ingenuity of our ancestors in...

Steelmaking ladles are essential in the steel production process, designed to transport and refine molten metal while withstanding extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion. They come in various types tailored for specific functions such as transferring, treating, casting, and precise pouring...

Steelmaking flux is crucial in producing high-quality steel, acting as a cleansing agent to remove impurities and enhance the metal's properties. Different types of fluxes are used for specific tasks during production, impacting impurity removal and refining processes while protecting...

Steel production for vehicles involves transforming iron ore into various steel grades with specific properties, balancing strength and formability. Innovations in manufacturing techniques ensure high-quality steel that meets automotive industry standards. The journey of steel from raw material to vehicle component...

The article explains the steel production process using a detailed steelmaking diagram, which visually breaks down each step from raw material preparation to finishing processes. It covers two main methods of steelmaking—Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS) and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)—and...

