Direct Reduced Iron
Direct Reduced Iron
Was ist Direct Reduced Iron?
Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) bezeichnet eine spezielle Form von Eisen. Dieses Eisen stellt in der Stahlproduktion und im Stahlhandel eine wichtige Zutat dar. Anders als herkömmliches Eisen wird DRI nicht in einem Hochofen gewonnen, sondern mit einem besonderen Verfahren. Genauer gesagt, nutzt man die Direktreduktion.
Das Verfahren der Direktreduktion
Bei der Direktreduktion nutzt man, wie der Name sagt, ein direktes Verfahren. Es wird nicht wie in einem Hochofen indirekt Eisen gewonnen. Stattdessen setzt man das Eisenerz direkt einem Reduktionsmittel aus. Dabei entsteht Direct Reduced Iron. Das Besondere: Das Eisen ist nahezu frei von Verschmutzungen. So kann man mit DRI sehr reinen Stahl herstellen.
Verwendung von Direct Reduced Iron
Direct Reduced Iron kommt in der Stahlindustrie zum Einsatz. Hier bewirkt es, dass der produzierte Stahl eine hohe Reinheit aufweist. Außerdem dient DRI als Ausgangsmaterial für die Weiterverarbeitung zu anderen Stahlerzeugnissen. Nicht zuletzt ist Direct Reduced Iron eine nachhaltiger Alternative zum herkömmlichen Hochofenverfahren. Es verbraucht weniger Energie und erzeugt weniger CO2.
Warum ist DRI wichtig?
Direct Reduced Iron bietet viele Vorteile. Es trägt zur Herstellung von hochreinem Stahl bei, der in vielen Bereichen benötigt wird. Dazu zählen etwa der Automobilbau, der Maschinenbau oder die Bauindustrie. Zudem ist die Produktion von DRI umweltfreundlicher als herkömmliche Verfahren. Deshalb nimmt seine Bedeutung in der Stahlindustrie und im Stahlhandel immer weiter zu.
Blog Posts with the term: Direct Reduced Iron

Steel making is a sophisticated process that turns iron ore into steel, involving methods like the Blast Furnace and Electric Arc Furnace to produce various grades of steel. The industry emphasizes sustainability by using additives and recycled materials while ensuring...

The article provides an overview of the steel making process, detailing how raw materials like iron ore, coke, and limestone are transformed into versatile and durable steel through a complex series of steps depicted in a flow diagram. It discusses...

The article provides an overview of the two main steelmaking routes: blast furnace (BF) and electric arc furnace (EAF), detailing their processes, economic considerations, environmental impacts, and technological advancements. It compares BF's large-scale production with high carbon emissions to EAF's...

Coke is crucial in steel production, providing heat and chemical reactions for smelting iron ore while also structuring the blast furnace. However, its use emits pollutants and CO2, contributing to environmental concerns....

The article "Introduction to Steelmaking from Pig Iron" explores the historical and modern processes of transforming pig iron into steel, including methods like the Bessemer Process, Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS), and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). It highlights the importance of...

Steel's origins trace back to meteoric iron and evolved with human discovery of smelting around 2500 BCE, leading from the Bronze Age into the Iron Age. The Bessemer Process in the mid-19th century revolutionized steel production, enabling mass production and...

The steelmaking industry is increasingly using natural gas to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Natural gas serves as a reducing agent in Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) processes, partially replaces coke in blast furnaces, fuels various types of industrial furnaces,...

Steel production is a highly energy-intensive process with significant environmental impacts, making the understanding and monitoring of energy consumption at each stage crucial for sustainability. Energy efficiency in steel manufacturing is essential for cost-effectiveness, competitiveness, and reducing carbon emissions, with...
The electric arc furnace (EAF) revolutionizes steel making by melting recycled scrap with high-power electric arcs, offering a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional blast furnaces. EAFs provide flexibility in production, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption, and allow...

The global steel industry, vital for infrastructure and economic development, is evolving in 2023 through innovation, sustainability efforts, and fierce competition. Dominated by China with six of the top ten producers, the sector highlights strategic growth driven by technological advancements...
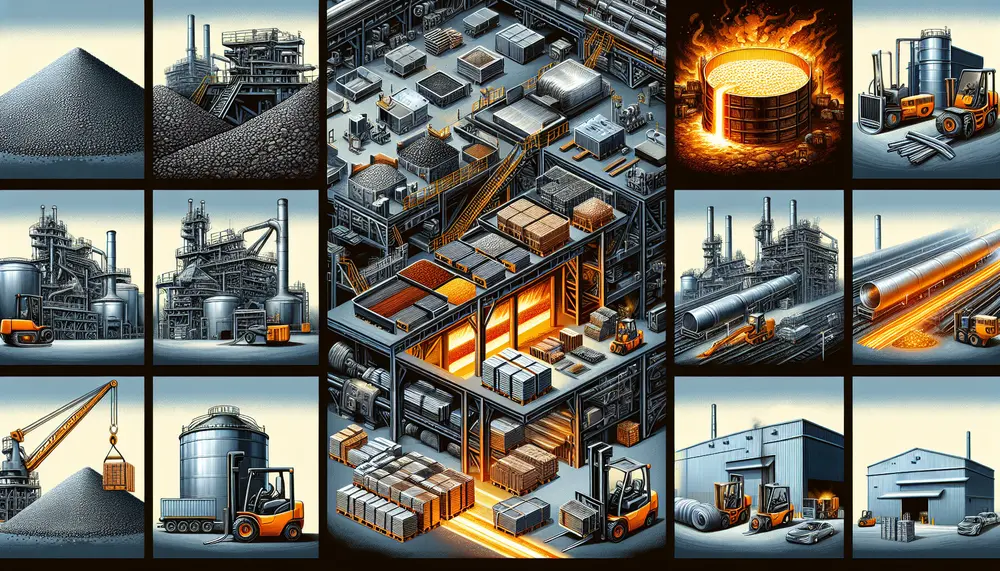

Steel production, a complex process involving several stages from mining of raw materials to creation of the final product, significantly impacts the price and sustainability of steel. Understanding this value chain is crucial for decision-making in the industry as it...

The article traces the history of steelmaking from early iron discoveries around 2,500 BCE to advanced techniques like Chinese cast iron production and Indian Wootz steel. It highlights key innovations such as smelting, forging by the Chalybes, and global influences...

Steel making involves complex chemical reactions to transform raw materials into high-quality steel, primarily through oxidation and reduction processes. Oxygen plays a crucial role in oxidizing impurities like carbon, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus, which are then removed as gases or...
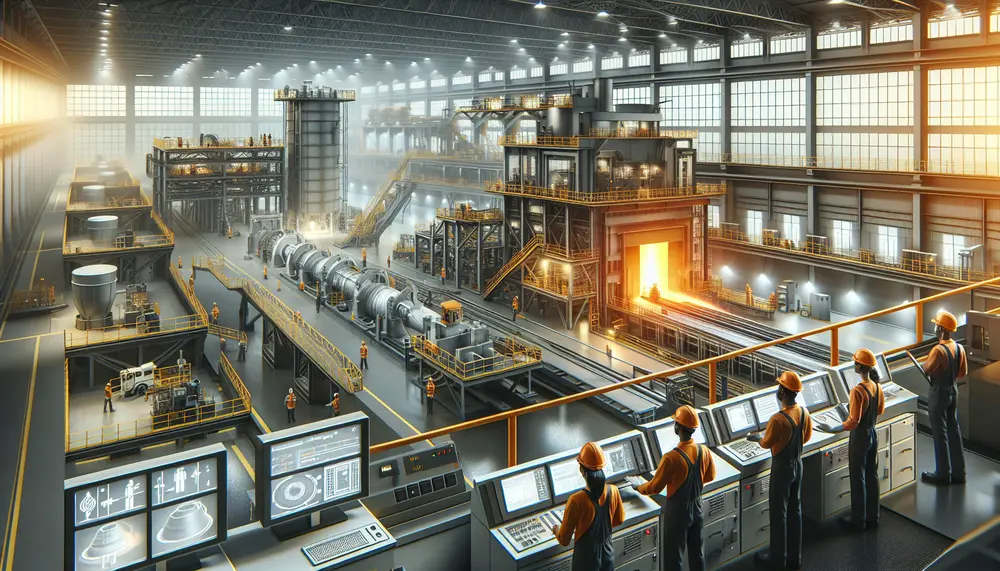

The article explains the importance of understanding a steelmaking flow chart, which outlines each step from raw material preparation to final products, aiding in efficiency and productivity. It details key components like raw materials (iron ore, limestone, coal), primary steps...

