Ductility
Ductility
Was ist Ductility?
Unter Ductility, auch als Verformbarkeit bekannt, versteht man die Fähigkeit eines Materials, sich unter Zugspannung stark zu verformen, ohne zu brechen. In der Stahlindustrie spielt diese Eigenschaft eine entscheidende Rolle.
Ductility in Bezug auf Stahlproduktion und Stahlhandel
In der Stahlproduktion und dem Stahlhandel ist die Ductility von entscheidender Bedeutung. Stahl mit hoher Ductility lässt sich gut formen und zu unterschiedlichen Strukturen, wie Brücken, Autos oder auch Möbeln, verarbeiten. Lehrmeister und Facharbeiter schätzen diese Eigenschaft, da sie eine hohe Flexibilität bei der Verarbeitung bietet.
Wie misst man Ductility?
Ductility lässt sich messen! Man nutzt dazu ein Prüfverfahren, bei dem die Probe durch Zugbeanspruchung verformt wird. Man registriert, wie viel sich die Probe dehnen lässt, bevor sie reißt. Dieser Wert ist ein Maß für ihre Ductility. Temperatur, Dauer der Belastung und die Art des Materials spielen dabei eine wichtige Rolle.
Warum ist Ductility wichtig?
Ductility ist ein wichtiger Indikator für die Qualität von Stahl. Ein stahlmetallurgisches Produkt mit hoher Ductility ermöglicht es, in der Herstellung und beim Einsatz großer Belastungen standzuhalten, ohne zu brechen. Damit gewährleistet es Sicherheit und eine lange Lebensdauer.
Blog Posts with the term: Ductility

Coke is crucial in steel production, providing heat and chemical reactions for smelting iron ore while also structuring the blast furnace. However, its use emits pollutants and CO2, contributing to environmental concerns....
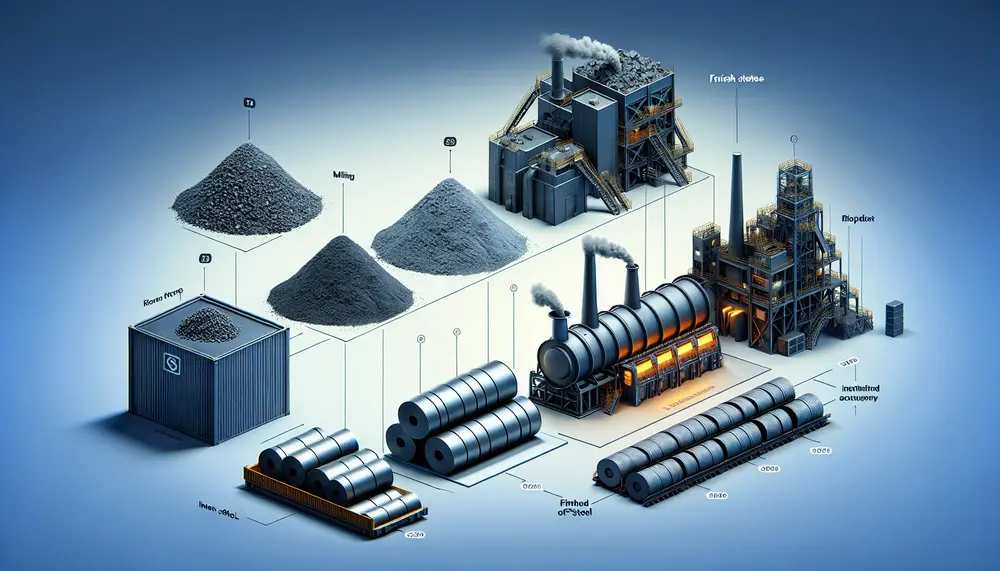
The steelmaking value chain is a complex process that transforms raw materials like iron ore, coking coal, and limestone into high-quality steel through strategic steps involving technological innovation to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Understanding this value chain helps...
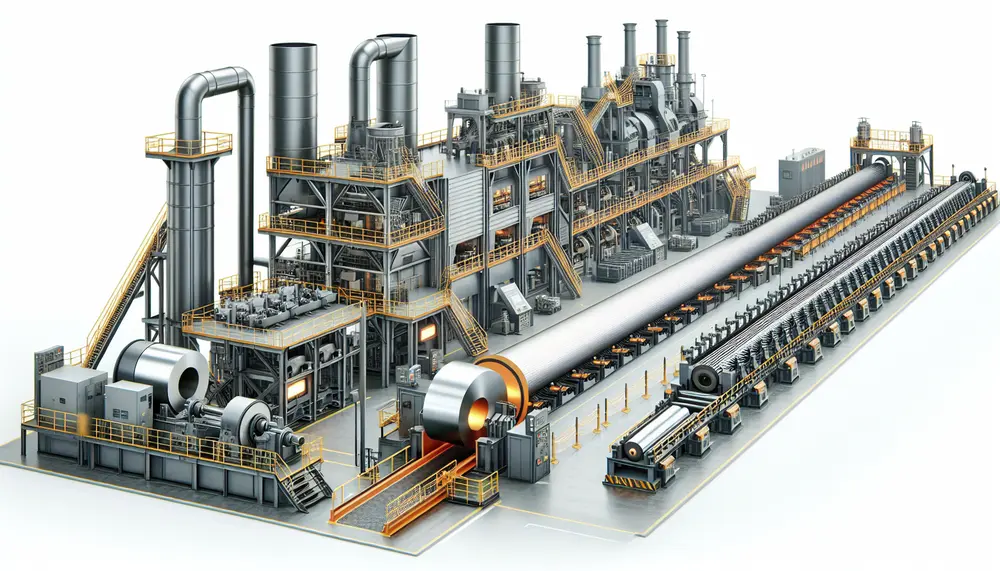
Steel manufacturing is a complex process that transforms iron ore into steel, involving precise heating and mixing to create different grades for various applications. The journey includes primary methods like Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS) and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), followed...

The Argon Oxygen Decarburization (AOD) process is a secondary steel making method that refines the composition of steel by reducing carbon content, using oxygen and inert gases like argon for controlled reactions. This technology allows for high-quality alloy production with...

The article traces the evolution of steelmaking from ancient techniques to significant medieval innovations, highlighting early methods like iron carburization and bloomery processes that evolved into more efficient practices with the introduction of blast furnaces. It also covers Renaissance advancements...

Steel making involves complex chemical reactions to transform raw materials into high-quality steel, primarily through oxidation and reduction processes. Oxygen plays a crucial role in oxidizing impurities like carbon, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus, which are then removed as gases or...

The article provides an overview of steel making, detailing its historical evolution and main processes such as ironmaking, primary and secondary steelmaking, casting, and forming; it highlights the importance of methods like the basic oxygen process and electric arc furnace...

Steel making technology has evolved from primitive forges to modern, efficient mills using methods like the Blast Furnace and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), which recycles scrap metal. Recent innovations aim at enhancing efficiency and sustainability with developments such as advanced...

The iron and steel industry is undergoing a new era of innovation, driven by advancements in automation, energy efficiency, and carbon reduction. Key trends include the use of AI and IoT for fully automated plants, advanced production technologies that require...

Steelmaking ladles are essential in the steel production process, designed to transport and refine molten metal while withstanding extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion. They come in various types tailored for specific functions such as transferring, treating, casting, and precise pouring...
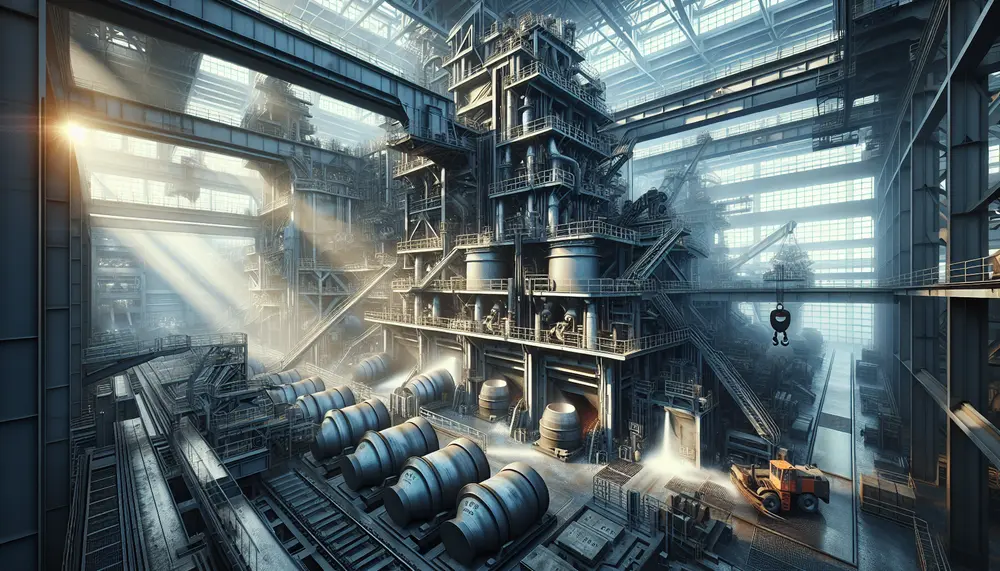
The steel making degassing process is essential for producing high-quality steel by removing dissolved gases like hydrogen, nitrogen, and carbon monoxide to prevent material defects. Vacuum degassing enhances the mechanical properties of steel, crucial for applications in construction and manufacturing,...

Steelmaking flux is crucial in producing high-quality steel, acting as a cleansing agent to remove impurities and enhance the metal's properties. Different types of fluxes are used for specific tasks during production, impacting impurity removal and refining processes while protecting...

Steel production for vehicles involves transforming iron ore into various steel grades with specific properties, balancing strength and formability. Innovations in manufacturing techniques ensure high-quality steel that meets automotive industry standards. The journey of steel from raw material to vehicle component...

Desulfurization in steelmaking is crucial for producing high-quality, durable steel by removing sulfur impurities that cause brittleness; advancements and techniques like desulfurizing agents, slag optimization, and vacuum treatment enhance this process while addressing challenges such as cost and environmental concerns....

