Manganese
Manganese
Was ist Manganese (Mangan)?
Manganese, auch bekannt als Mangan, ist ein chemisches Element mit dem Symbol Mn und der Ordnungszahl 25. Es ist ein silber-graues Metall, das in der Erdkruste zu finden ist. Mangan ist bekannt für seine außergewöhnliche Härte und seine Fähigkeit, Eisen und Stahl zu verstärken.
Manganese in der Stahlproduktion
In der Produktion von Stahl spielt Manganese eine sehr wichtige Rolle. Warum? Stellen Sie sich Manganese als den "Helfer" vor, der den Stahl stärker und widerstandsfähiger gegen Abnutzung macht. Es ist der Bestandteil, der dem Stahl erlaubt, seine Form zu behalten, ohne zu brechen oder zu verbiegen, selbst unter hohem Druck und in extremen Temperaturen. Kurz gesagt, ohne Manganese wäre Stahl einfach nicht so stark und haltbar wie er ist.
Manganese im Stahlhandel
Da Manganese so wichtig für die Herstellung von Stahl ist, hat es auch einen großen Einfluss auf den Handel mit Stahl. Händler, die Stahl verkaufen oder kaufen, achten stark auf den Manganese-Gehalt im Stahl. Je höher der Manganese-Gehalt, desto wertvoller ist in der Regel der Stahl, da er dann stärker und langlebiger ist. Deshalb ist Manganese ein wichtiger Faktor für die Bestimmung des Preises von Stahl auf dem Markt.
Zusammenfassung
Ohne Manganese wäre Stahl einfach nicht so stark und langlebig wie wir ihn kennen. Es spielt eine absolut wichtige Rolle in der Produktion von Stahl und hat daher auch einen großen Einfluss auf den Stahlhandel. Manganese ist ein wahrer Freund und Helfer in der Welt des Stahls.
Blog Posts with the term: Manganese
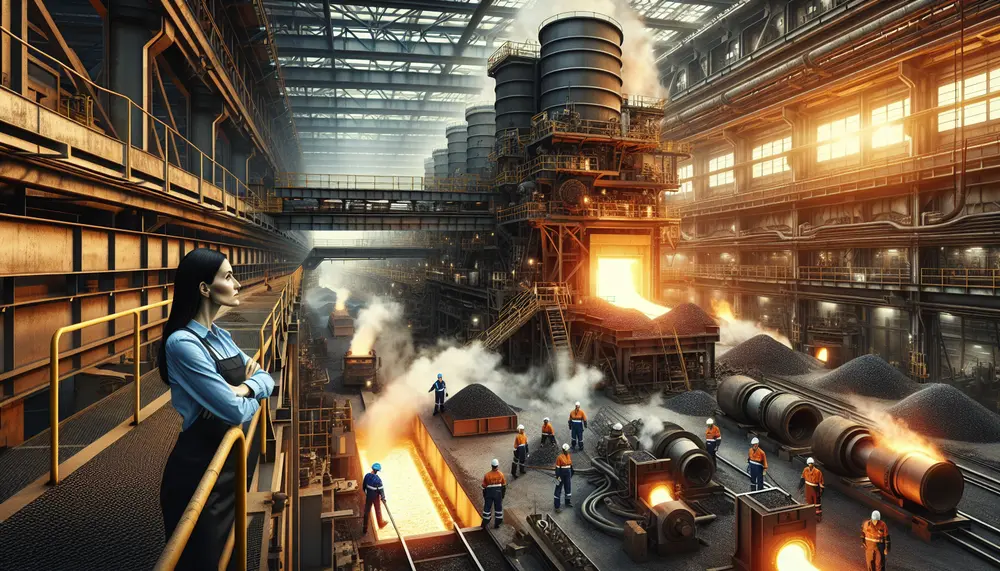

The article "Introduction to Steelmaking from Pig Iron" explores the historical and modern processes of transforming pig iron into steel, including methods like the Bessemer Process, Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS), and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). It highlights the importance of...
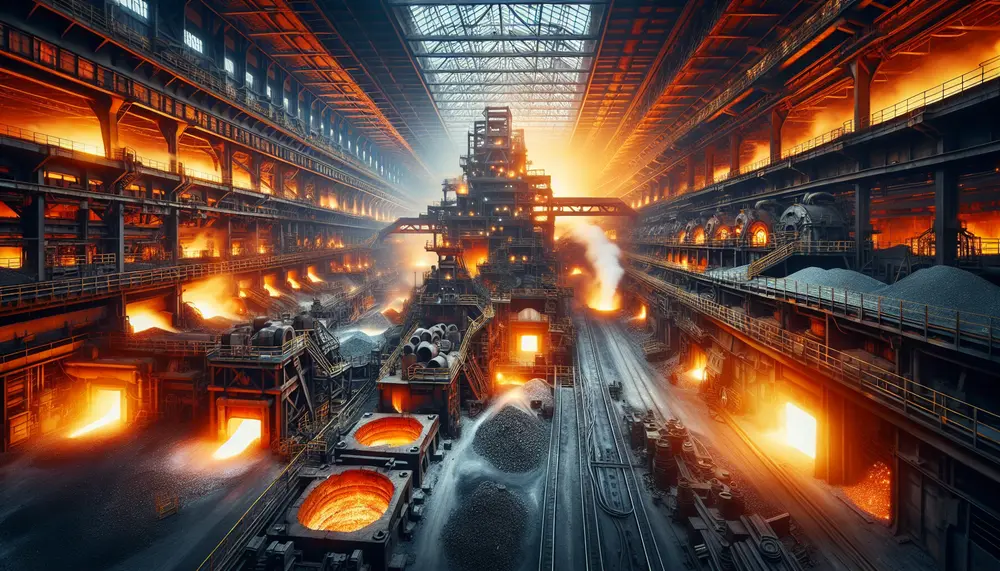

The Bessemer process, developed by Henry Bessemer in the 1850s, revolutionized steel production by efficiently removing impurities from molten pig iron using blown air and enabling mass production. This innovation significantly reduced costs and time for steel manufacturing, facilitating industrial...

Steel, an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, is a crucial material in modern construction and manufacturing due to its strength, flexibility, and durability. The process of making steel involves extracting iron ore, purifying it through beneficiation processes, smelting...
Steel manufacturing is a complex process that transforms iron ore into steel, involving precise heating and mixing to create different grades for various applications. The journey includes primary methods like Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS) and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), followed...

Steel's origins trace back to meteoric iron and evolved with human discovery of smelting around 2500 BCE, leading from the Bronze Age into the Iron Age. The Bessemer Process in the mid-19th century revolutionized steel production, enabling mass production and...
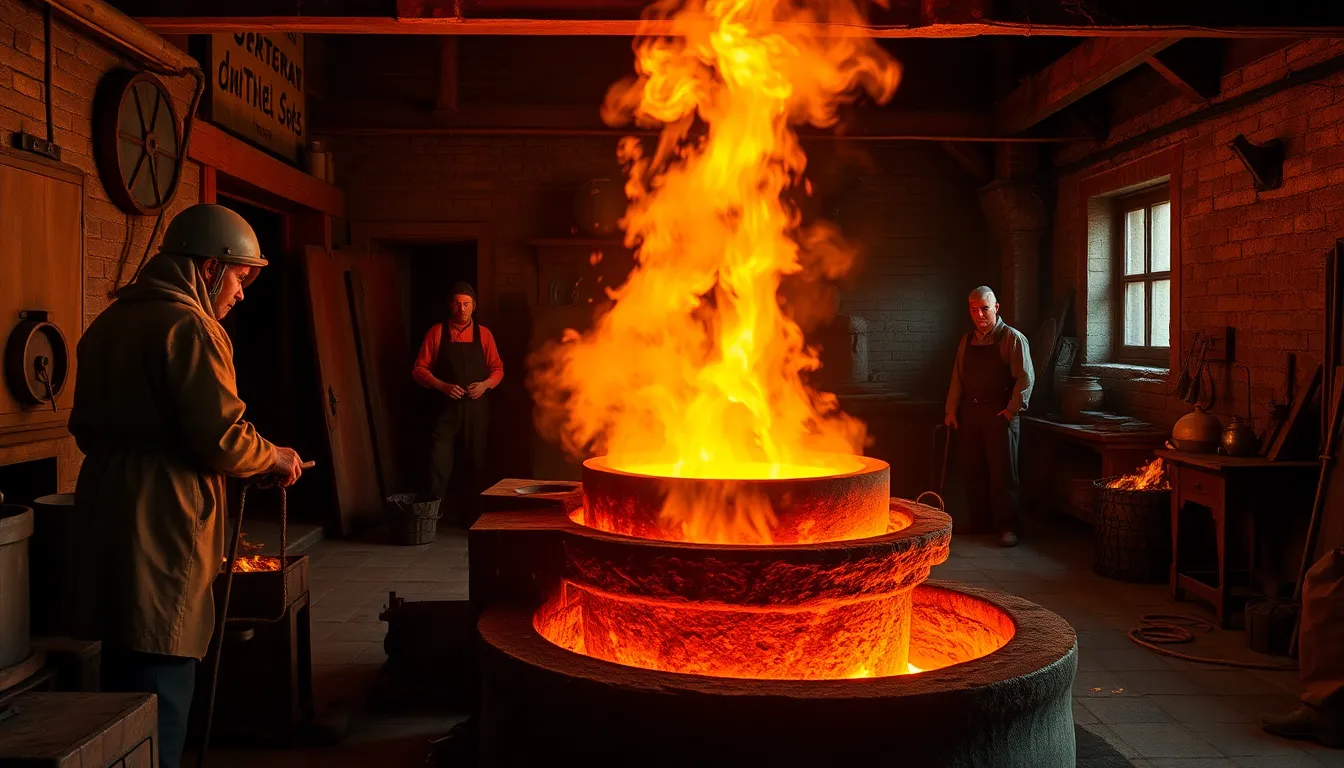

The article traces the evolution of steelmaking from ancient techniques to significant medieval innovations, highlighting early methods like iron carburization and bloomery processes that evolved into more efficient practices with the introduction of blast furnaces. It also covers Renaissance advancements...
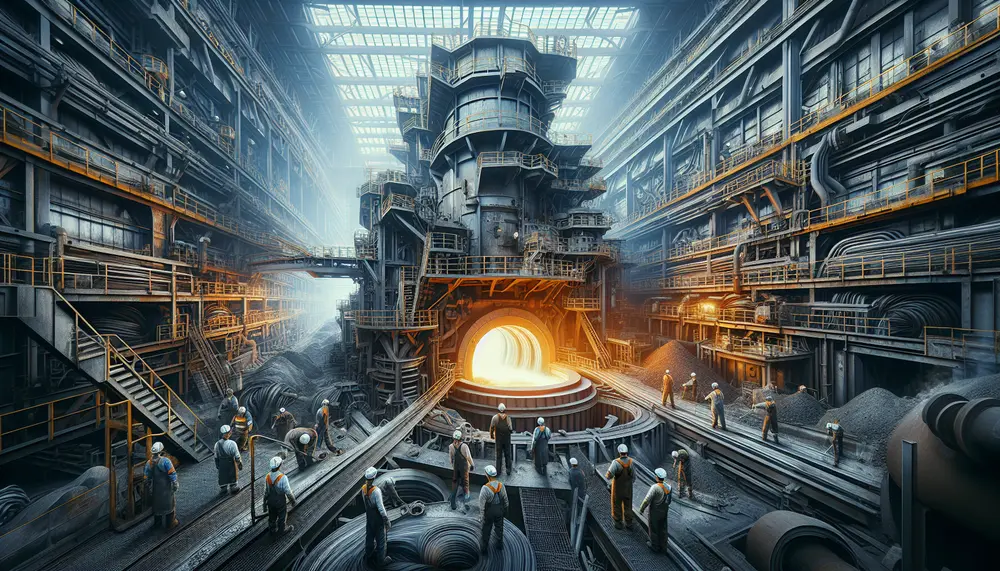

The Open Hearth Process is a traditional steelmaking method that involves converting iron into steel using an open hearth furnace, which allows air to flow over the mixture and facilitates chemical reactions necessary for purification. This process utilizes regenerative heating...

The article traces the history of steelmaking from early iron discoveries around 2,500 BCE to advanced techniques like Chinese cast iron production and Indian Wootz steel. It highlights key innovations such as smelting, forging by the Chalybes, and global influences...

Steel making involves complex chemical reactions to transform raw materials into high-quality steel, primarily through oxidation and reduction processes. Oxygen plays a crucial role in oxidizing impurities like carbon, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus, which are then removed as gases or...

The article "Introduction to Ancient Steel Making" explores the historical context, key techniques, and materials used in ancient steel production across various civilizations. It highlights how early methods influenced modern steel making and underscores the ingenuity of our ancestors in...

Steelmaking ladles are essential in the steel production process, designed to transport and refine molten metal while withstanding extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion. They come in various types tailored for specific functions such as transferring, treating, casting, and precise pouring...
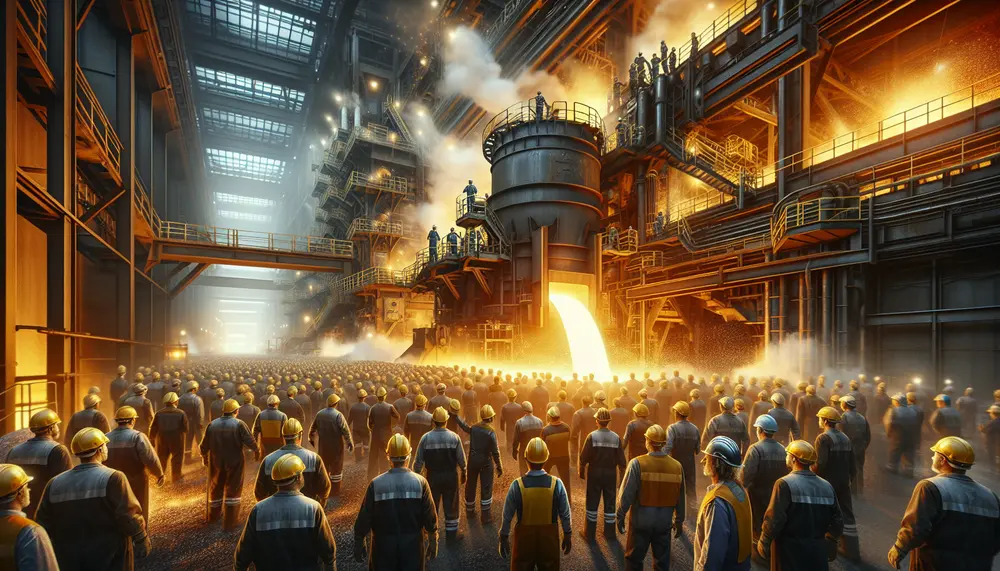

The Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) process, developed in the mid-20th century by Robert Durrer, revolutionized steel production by using pure oxygen to convert molten iron into high-quality steel efficiently. This method involves charging a furnace with molten iron and scrap...
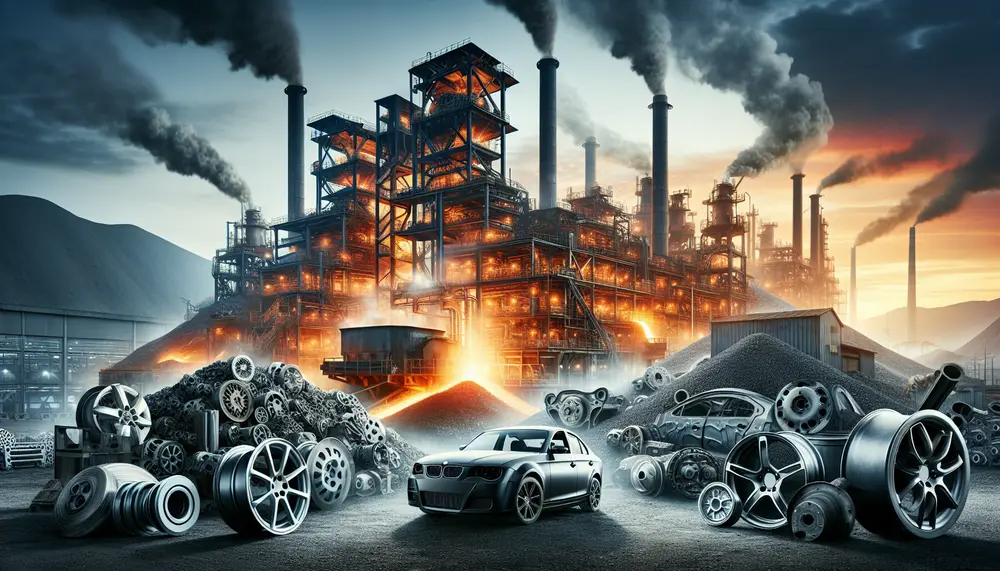

Steel production for vehicles involves transforming iron ore into various steel grades with specific properties, balancing strength and formability. Innovations in manufacturing techniques ensure high-quality steel that meets automotive industry standards. The journey of steel from raw material to vehicle component...
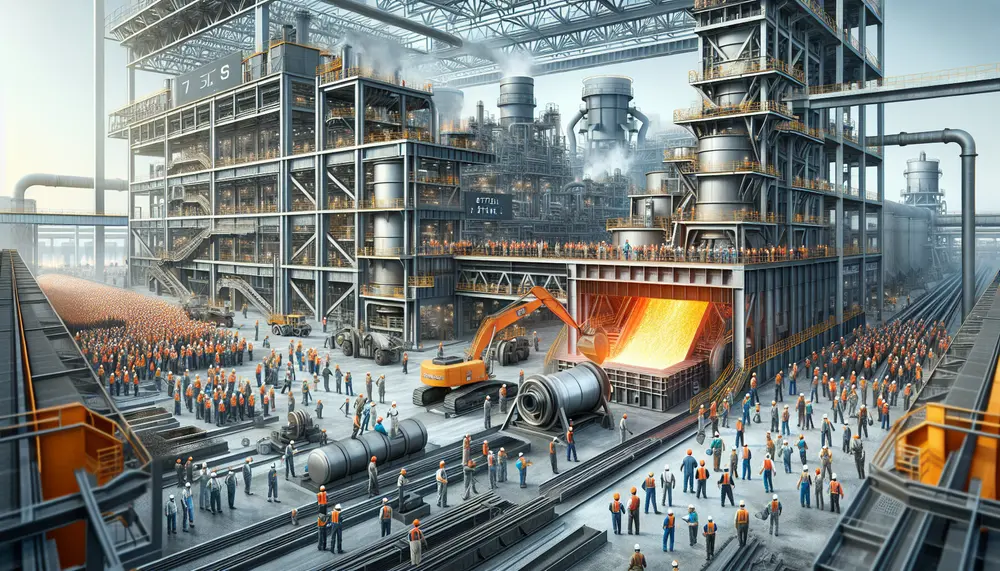

The article explains the steel production process using a detailed steelmaking diagram, which visually breaks down each step from raw material preparation to finishing processes. It covers two main methods of steelmaking—Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS) and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)—and...
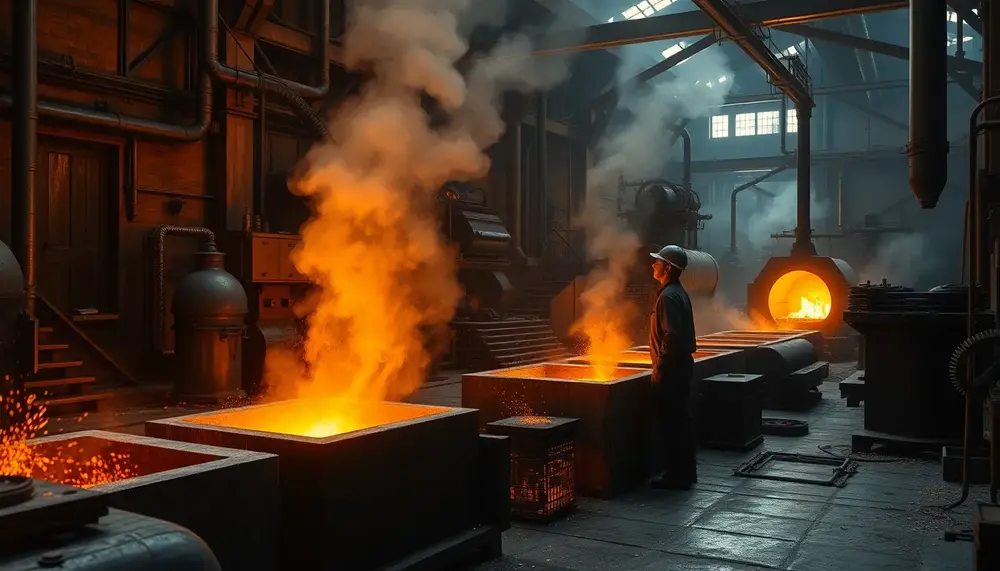

Henry Bessemer revolutionized steel production in the 19th century with his innovative process, enabling mass production of stronger, affordable steel and fueling industrial growth. By efficiently removing impurities through oxygen blasts, his method drastically reduced costs and transformed steel into...
