Non-metallic inclusions
Non-metallic inclusions
Definition von Non-metallic inclusions
Wenn wir den Begriff Non-metallic inclusions hören, kann es zunächst ein wenig verwirrend sein. Aber, keine Angst! Wir sind hier, um es zu erklären. Non-metallic inclusions sind kleine, nichtmetallische Partikel, die sich in Metallen, insbesondere Stahl, festsetzen können. Sie können aus Oxiden, Sulfiden, Silikaten oder einer Mischung dieser Materialien bestehen. Du kannst dir Non-metallic inclusions wie Sand in einem Meer von Metall vorstellen.
Non-metallic inclusions und Stahlherstellung
Im Kontext der Stahlproduktion sind Non-metallic inclusions oft unerwünscht. Sie können die Eigenschaften des fertigen Stahls und seine Leistung in der Anwendung beeinflussen. Daher ist es wichtig, die Inclusions in der Produktion so gut wie möglich zu reduzieren. In jedem Fall unternehmen Stahlwerke erhebliche Anstrengungen, um die Menge dieser Inclusions zu reduzieren.
Arten von Non-metallic inclusions
Es gibt verschiedene Arten von Non-metallic inclusions. Die gebräuchlichsten sind Oxid-Inclusions, Sulfid-Inclusions und Silikat-Inclusions. Oxide sind üblicherweise das Ergebnis von Sauerstoffreaktionen in der Schmelze, während Sulfide meist durch Schwefelverunreinigungen entstehen.
Umgang mit Non-metallic inclusions
Die Steel producers haben Techniken und Verfahren entwickelt, um Non-metallic inclusions zu reduzieren oder zu entfernen. Ein gebräuchlicher Ansatz ist das Nutzen von Filtern und Schlacken, die die Inclusions aufnehmen. Darüber hinaus gibt es Prozesse, die die Inclusions verkleinern, um deren Auswirkungen zu minimieren.
Non-metallic inclusions und Stahlhandel
Im Stahlhandel ist es wichtig, die Menge der Non-metallic inclusions zu kennen. Kunden wollen Stahl von hoher Qualität und in vielen Fällen kann ein hoher Gehalt an Inclusions auf Probleme hinweisen. Darum prüfen Stahlhändler oft auf das Vorhandensein und die Menge von Inclusions.
Blog Posts with the term: Non-metallic inclusions

The article provides an overview of steel making, detailing its historical evolution and main processes such as ironmaking, primary and secondary steelmaking, casting, and forming; it highlights the importance of methods like the basic oxygen process and electric arc furnace...
The steel making degassing process is essential for producing high-quality steel by removing dissolved gases like hydrogen, nitrogen, and carbon monoxide to prevent material defects. Vacuum degassing enhances the mechanical properties of steel, crucial for applications in construction and manufacturing,...

The article provides a detailed overview of the steelmaking process, starting from raw material extraction to final product creation. It emphasizes the importance of understanding each stage and the key materials involved—iron ore, coal, limestone, and scrap metal—to produce high-quality...

RH technology, initially developed for hydrogen removal in steel making, now plays a crucial role in secondary refining and purification to ensure high-quality steel production. Key advancements like oxygen lances, powder injection systems, the RH-TOP system, and modern vacuum pumps...

Secondary steelmaking refines and adjusts the composition of steel to meet specific standards, involving processes like deoxidation, desulfurization, decarburization, alloying, and degassing. It is crucial for producing high-quality steel with desired properties such as strength and corrosion resistance. The role of...

The Ladle Metallurgy Furnace (LMF) is a crucial advancement in modern steel production, allowing for precise control over the chemical composition and temperature of molten steel to produce high-quality products. This technology involves transferring liquid steel into a specialized furnace...

The concept of steelmaking grade is crucial in determining the quality and properties of steel, influencing efficiency, durability, and safety across various industries. Steel grades are classified based on chemical composition and production processes, with advancements in technology and global...
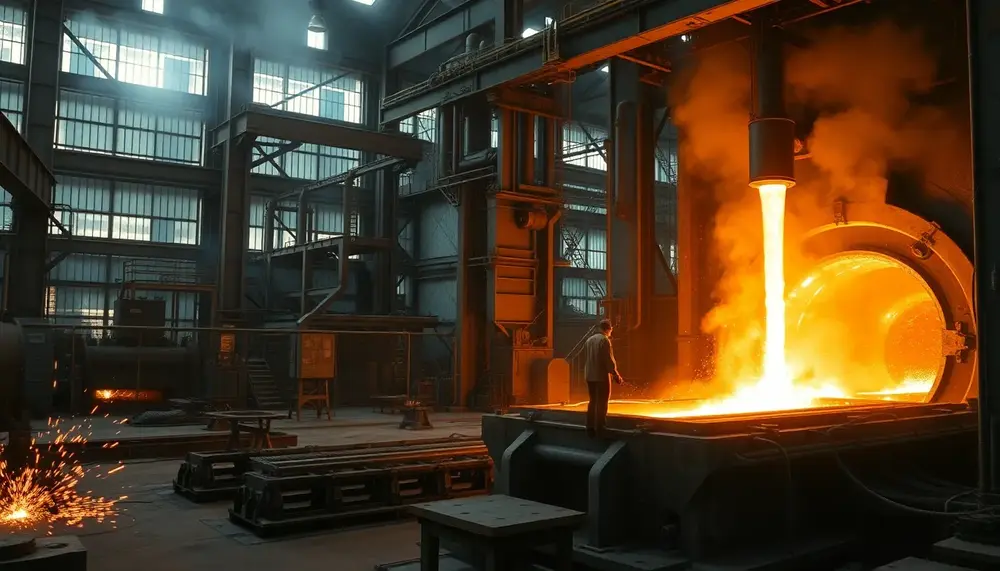

The article explores the steel industry's complexity, highlighting PDFs as essential guides for understanding processes like raw material preparation, ironmaking, and refining. It emphasizes the blast furnace's critical role in transforming raw materials into molten iron through efficient chemical reactions...
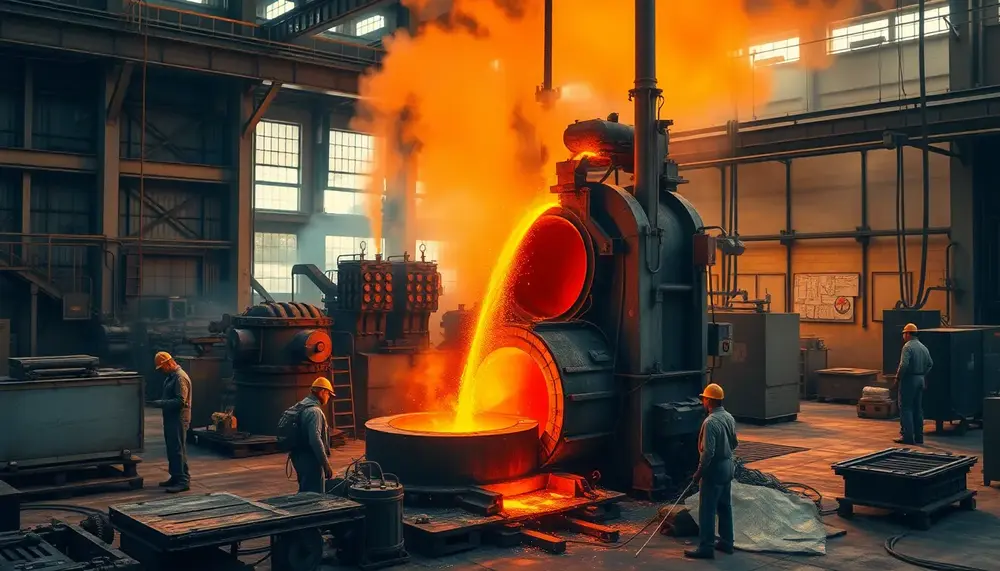

Steel refining transforms raw materials into high-quality steel by removing impurities and enhancing properties through advanced techniques like BOF, EAF, and DRI. Modern innovations ensure precision, efficiency, sustainability, and tailored applications across industries while addressing environmental challenges....
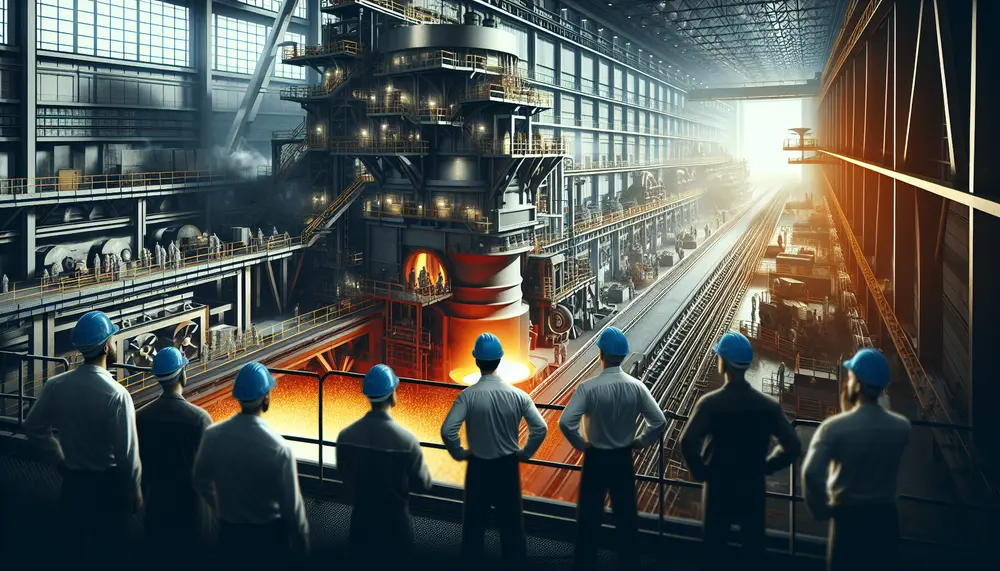

The steelmaking tundish is a critical intermediary in the continuous casting process, serving as both a reservoir and buffer for molten steel while facilitating controlled flow and cleanliness to enhance final product quality. Its design has evolved since the 1950s,...
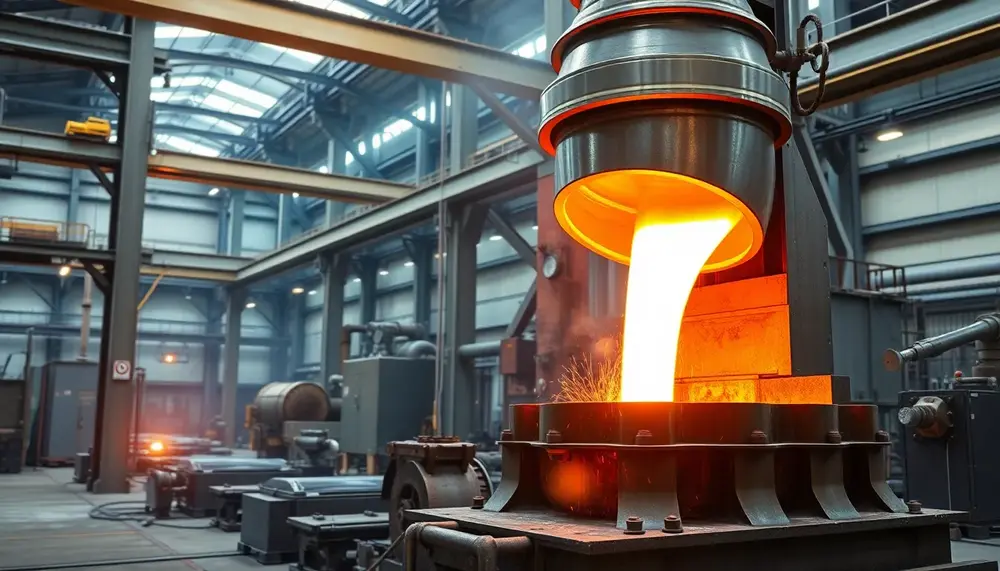

Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) revolutionizes steel-making by enabling ultra-pure alloys through precise melting, impurity removal in a vacuum, and real-time composition control. Recent innovations like advanced monitoring systems, hybrid techniques, and energy-efficient designs enhance material quality while promoting sustainability for...
Steelmaking combines science and engineering to transform raw materials into tailored steel products through precise control of temperature, composition, and reactions. Its evolution reflects human innovation, from ancient smelting techniques to modern sustainable methods driven by advanced theoretical principles like...
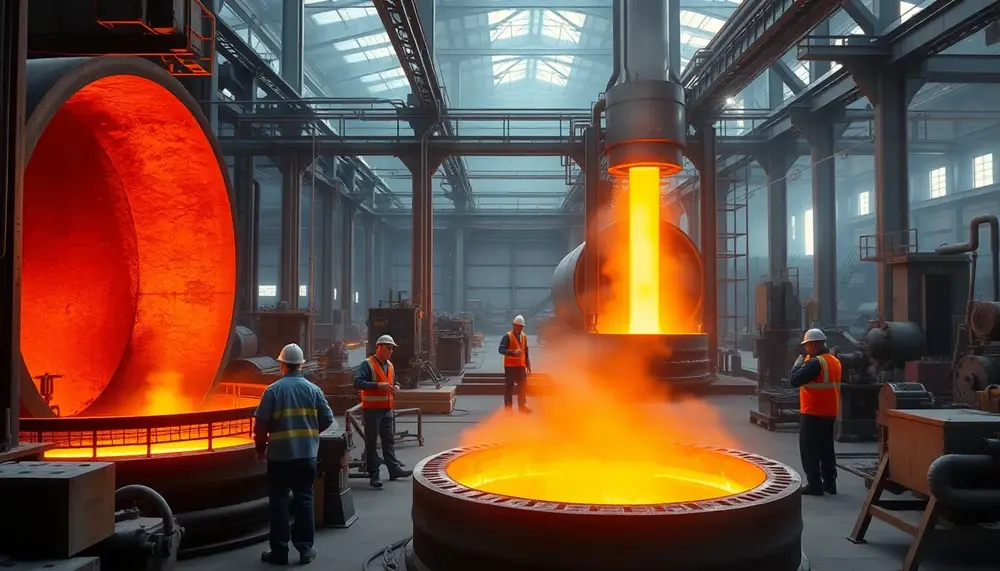

Secondary steelmaking refines and customizes steel after primary production, enabling precise control over composition and purity to meet modern industry demands. Key stages include deslagging, alloy addition, temperature adjustment, degassing, inclusion modification, and homogenization using advanced technologies like ladle furnaces...
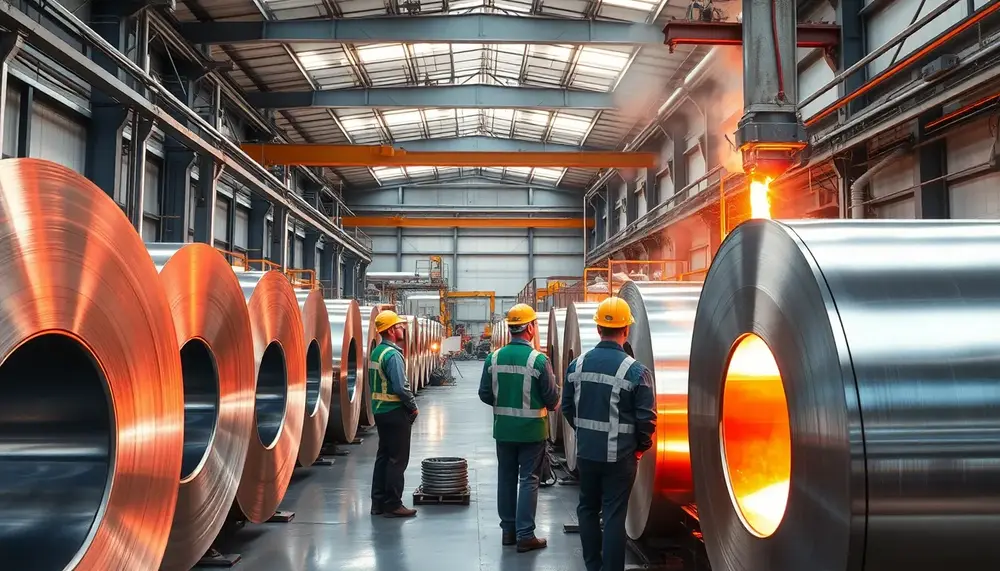

Stainless steel manufacturing is a precise, multi-stage process combining advanced technology and strict quality control to produce durable, corrosion-resistant materials....

