Water-cooled
Water-cooled
Was bedeutet 'Water-Cooled' in der Stahlproduktion und im Stahlhandel?
Die Bezeichnung 'water-cooled' oder 'wassergekühlt' wird in der Stahlproduktion und im Stahlhandel oft verwendet. Dieses Wort bezieht sich auf den Prozess, bei dem Wasser zur Abkühlung von heißen Stahlprodukten verwendet wird.
Warum ist 'Water-Cooled' wichtig?
Bei der Stahlproduktion erreichen die Materialien extrem hohe Temperaturen. Ohne angemessene Kühlung kann dies zu Schäden oder sogar zur Zerstörung der Stahlprodukte führen. Der 'Water-Cooled' Prozess hilft, das Material schnell und effizient auf eine sichere Temperatur zu bringen. Zudem ist Wasser wegen seiner hohen Wärmekapazität zum Kühlen hervorragend geeignet.
'Water-Cooled' in verschiedenen Stahlproduktionsprozessen
'Water-Cooled' wird in einer Reihe von Stahlproduktionsprozessen verwendet. Zum Beispiel, bei der Herstellung von Stahlplatten, ist es üblich, dass die heißen Platten durch Wasserstrahlen abgekühlt werden. Auch bei der Herstellung von Stahlrohren wird oft ein 'water-cooled' Verfahren angewandt, um die Produkte zu stabilisieren und sie für den Versand vorzubereiten. Bei komplexeren Herstellungsverfahren, wie dem, das bei Stahldrähten angewendet wird, kann ein kontinuierlicher 'Water-Cooled' Prozess erforderlich sein.
Die Rolle von 'Water-Cooled' im Stahlhandel
Im Stahlhandel ist 'Water-Cooled' ebenfalls ein wichtiger Aspekt. Die Qualität und Haltbarkeit von Stahl hängen stark von der richtigen Kühlung während der Produktion ab. Produktkäufer suchen oft gezielt nach 'water-cooled' Stahlprodukten, da diese tendenziell eine höhere Qualität und eine längere Lebensdauer haben.
Blog Posts with the term: Water-cooled

Steel making is a sophisticated process that turns iron ore into steel, involving methods like the Blast Furnace and Electric Arc Furnace to produce various grades of steel. The industry emphasizes sustainability by using additives and recycled materials while ensuring...
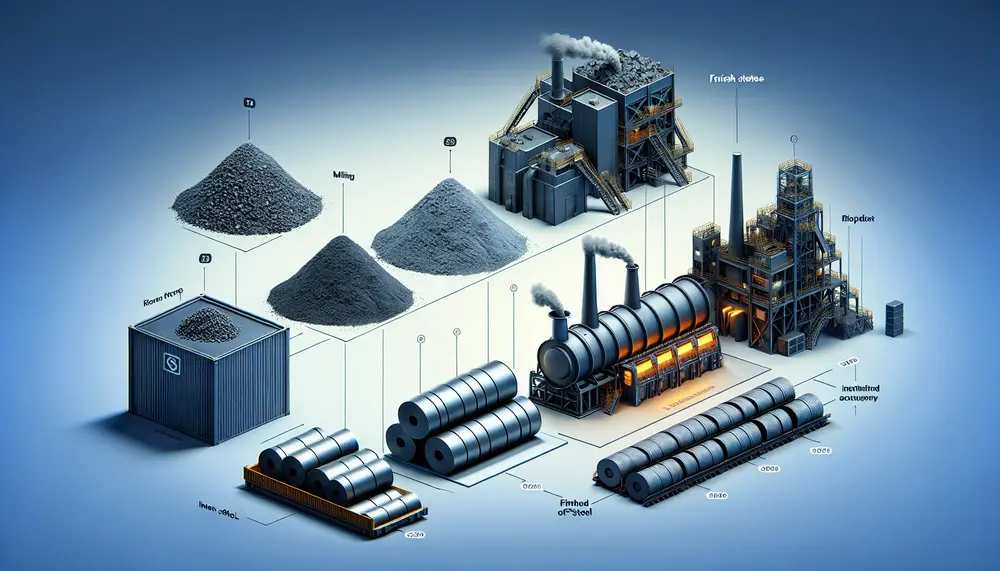
The steelmaking value chain is a complex process that transforms raw materials like iron ore, coking coal, and limestone into high-quality steel through strategic steps involving technological innovation to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Understanding this value chain helps...

Steel, an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon, is a crucial material in modern construction and manufacturing due to its strength, flexibility, and durability. The process of making steel involves extracting iron ore, purifying it through beneficiation processes, smelting...
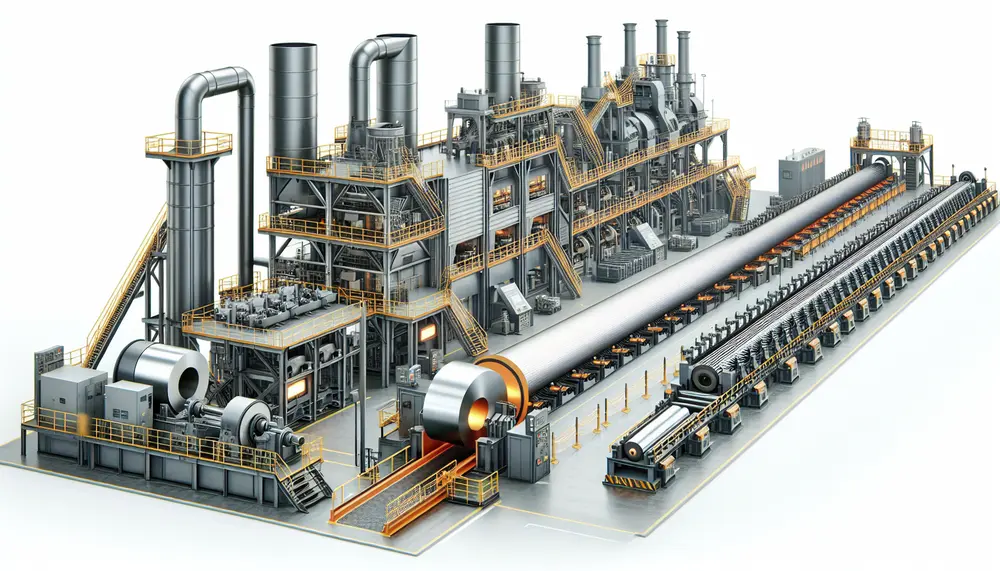
Steel manufacturing is a complex process that transforms iron ore into steel, involving precise heating and mixing to create different grades for various applications. The journey includes primary methods like Basic Oxygen Steelmaking (BOS) and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF), followed...
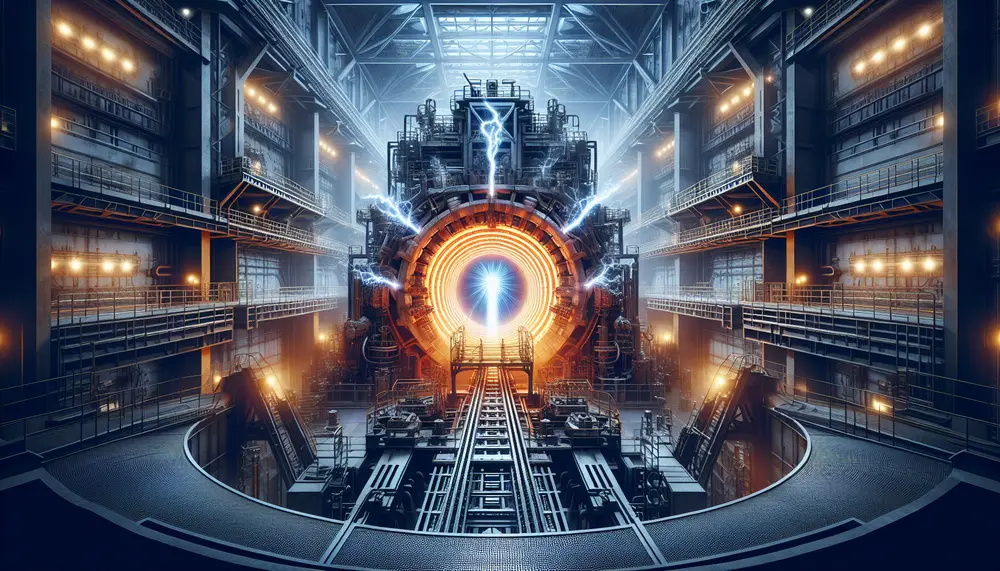
The electric arc furnace (EAF) revolutionizes steel making by melting recycled scrap with high-power electric arcs, offering a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional blast furnaces. EAFs provide flexibility in production, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption, and allow...

The article traces the history of steelmaking from early iron discoveries around 2,500 BCE to advanced techniques like Chinese cast iron production and Indian Wootz steel. It highlights key innovations such as smelting, forging by the Chalybes, and global influences...

The Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) process, developed in the mid-20th century by Robert Durrer, revolutionized steel production by using pure oxygen to convert molten iron into high-quality steel efficiently. This method involves charging a furnace with molten iron and scrap...

The article provides a detailed overview of the steelmaking process, starting from raw material extraction to final product creation. It emphasizes the importance of understanding each stage and the key materials involved—iron ore, coal, limestone, and scrap metal—to produce high-quality...

Steel manufacturing from scrap is a sustainable process that reduces environmental impact and conserves resources. It involves collection, separation, melting in an electric arc furnace, refining to remove impurities, adding alloy elements, and casting into new products; recycling steel offers...

India's steel industry utilizes rich iron ore resources and advanced technology, adopting innovative methods like automation for efficient production. Government policies support sustainable practices in this key economic sector that drives growth and employment....

The article provides a comprehensive guide to steel production, simplifying core concepts for beginners and detailing key processes such as the Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) and Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) methods. It covers essential steps from ironmaking to finishing, offering...

A steel product is an item predominantly made of steel, known for its durability and versatility across industries, with a wide range of forms and applications. Understanding these products involves knowledge of the production process from raw materials to finished...
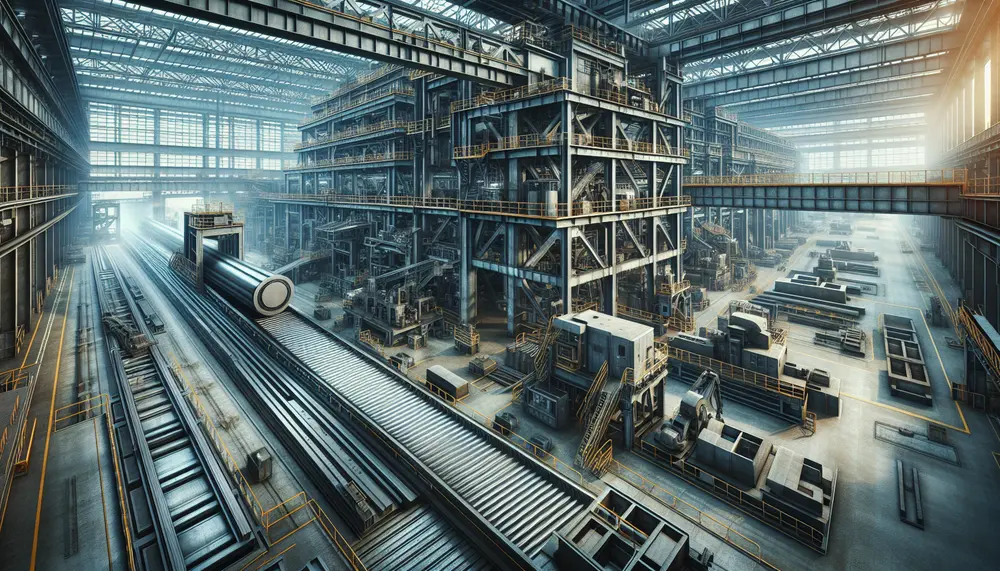
Steel manufacturing is a complex, multi-stage process that transforms raw materials into the durable metal essential for modern infrastructure. It begins with extracting iron ore and progresses through various phases including blast furnace operation and primary steelmaking methods like Basic...

The Ladle Metallurgy Furnace (LMF) is a crucial advancement in modern steel production, allowing for precise control over the chemical composition and temperature of molten steel to produce high-quality products. This technology involves transferring liquid steel into a specialized furnace...

