Non-renewable resources
Non-renewable resources
Was sind "Non-renewable resources"?
Der Begriff "Non-renewable resources", also nicht erneuerbare Ressourcen, bezeichnet natürliche Ressourcen, die sich in der Natur nicht oder nur sehr langsam erneuern. Diese umfassen fossile Brennstoffe wie Kohle, Erdöl und Erdgas sowie atomare Energiequellen und bestimmte Arten von Erzen. Im Kontext der Stahlproduktion und des Stahlhandels sind es insbesondere die Eisenerze, die als nicht erneuerbare Ressourcen gelten.
Die Rolle von "Non-renewable resources" in der Stahlproduktion und im Stahlhandel
Stahl ist ein aus Eisen und Kohlenstoff hergestelltes Material. Das Eisen, das zur Herstellung von Stahl benötigt wird, stammt aus Eisenerz, einer nicht erneuerbaren Ressource, die in der Erdkruste gelegen ist. Eisenerz ist die grundlegende Rohstoffquelle für die Stahlproduktion. Jede Tonne produzierten Stahls benötigt etwa 1,6 Tonnen Eisenerz. Daher spielt Eisenerz eine zentrale Rolle in der Stahlindustrie und seinem Handel.
Die Bedeutung der Nachhaltigkeit
Die Tatsache, dass Eisenerz eine nicht erneuerbare Ressource ist, wirft Fragen zur Nachhaltigkeit der Stahlproduktion und des Stahlhandels auf. Aufgrund der begrenzten Verfügbarkeit von Eisenerz müssen Stahlproduzenten effiziente Methoden zur Nutzung dieser Non-renewable resources entwickeln und dabei den Umweltschutz beachten. Vom Bergbau bis zur Stahlherstellung sind nachhaltige Praktiken und die Reduzierung des Ressourcenverbrauchs essentiell.
Alternativen zu "Non-renewable resources"
Halten wir uns die begrenzte Verfügbarkeit von Eisenerz vor Augen, gewinnen alternative Verfahren zur Stahlgewinnung immer mehr an Bedeutung. Recycling und der Einsatz von alternativen Rohstoffen sind zwei vielversprechende Ansätze. Bereits heute stammt ein beträchtlicher Teil des verwendeten Stahls aus Recycling. In Zukunft könnte der Anteil weiter steigen und so die Abhängigkeit von nicht erneuerbaren Ressourcen reduzieren.
Blog Posts with the term: Non-renewable resources

The African steel industry is growing and diverse, with varying levels of resource availability and technological sophistication across countries. It plays a crucial economic role by stimulating growth in other sectors, creating jobs, contributing to GDP, reducing import dependency, and...
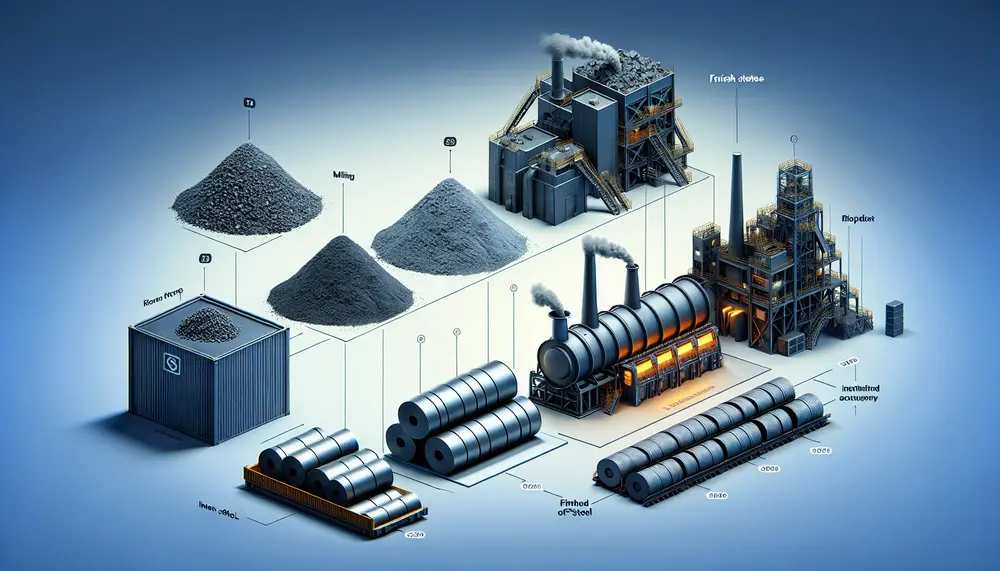
The steelmaking value chain is a complex process that transforms raw materials like iron ore, coking coal, and limestone into high-quality steel through strategic steps involving technological innovation to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Understanding this value chain helps...

Steel production for vehicles involves transforming iron ore into various steel grades with specific properties, balancing strength and formability. Innovations in manufacturing techniques ensure high-quality steel that meets automotive industry standards. The journey of steel from raw material to vehicle component...

Steel production is crucial to New Zealand's economy, utilizing local ironsand for high-quality steel and centered around the Glenbrook Steel Mill. The industry faces challenges such as energy costs and global competition but offers advantages like job creation and technological...

Steel making transforms iron ore into steel using blast furnaces or electric arc furnaces, involving processes like smelting and carbon adjustment to achieve desired properties. The production includes primary methods like Basic Oxygen Steelmaking and Electric Arc Furnace, followed by...

Steel production transforms raw materials like iron ore, coal, and limestone into steel through high-temperature processes in a factory. This complex journey from earth-bound elements to the final product is essential for construction and manufacturing industries, with each material playing...

Henry Bessemer revolutionized steel production by inventing a process that made mass production of high-quality steel possible, significantly reducing costs and impacting various industries. His invention was spurred by his early inventive spirit and lack of formal education, leading to...

Hydrogen steelmaking offers a sustainable alternative to traditional methods by using hydrogen as a reducing agent, significantly cutting carbon emissions and enhancing product quality. This method not only reduces the environmental impact but also supports integration with renewable energy sources,...

Green steel, produced with methods that reduce or eliminate CO2 emissions, is vital for environmental sustainability and the future of the industry amid climate change. The shift to renewable energy in steel production aligns with global trends towards a greener...

Sustainable steel production aims to minimize environmental impact through energy conservation, increased recycling, and innovative technologies like electric arc furnaces and hydrogen use. The industry faces challenges such as high energy consumption and carbon emissions but is exploring eco-friendly innovations...
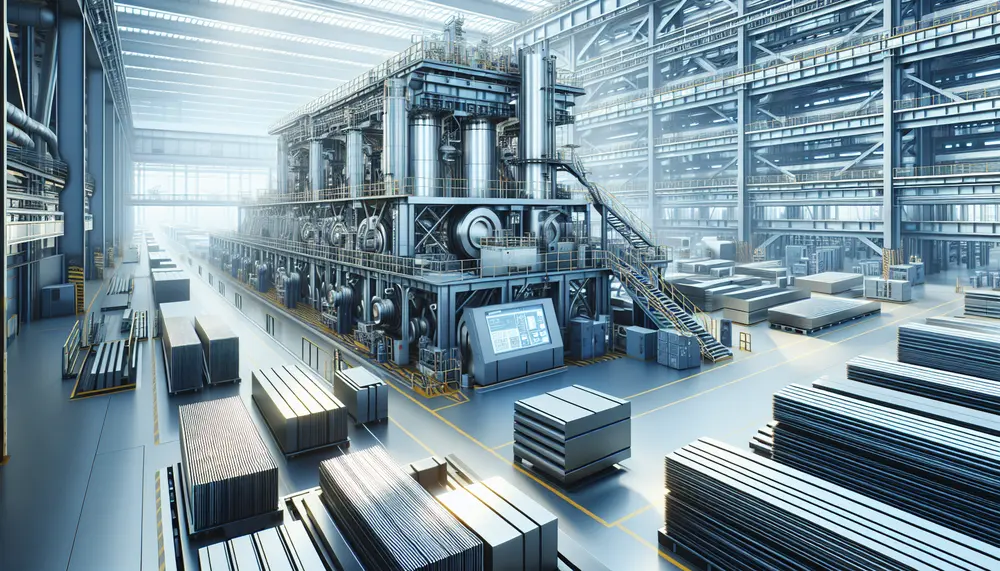
Steel production technology has evolved significantly, with the industry now using advanced methods like blast furnaces and electric arc furnaces to meet global demands. Technological improvements have enhanced quality, efficiency, and sustainability in steel making. The future of steel production focuses...

The steel making process transforms iron ore into a vital and robust material through complex technical procedures, reflecting human ingenuity and progress. This journey from extraction to the final product involves meticulous steps including smelting in blast furnaces, oxidation for...
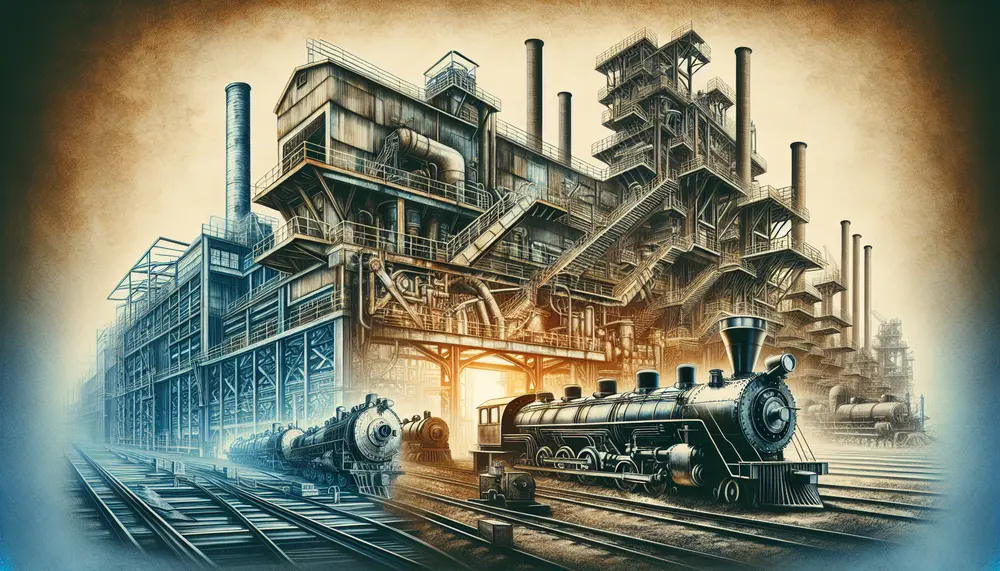
The evolution of steelmaking has progressed from labor-intensive early methods to advanced technologies like the Basic Oxygen Steelmaking and Electric Arc Furnaces, enhancing efficiency and sustainability. The once-dominant Bessemer Process was superseded due to its limitations in controlling chemical composition...

The steelmaking industry is evolving with trends like sustainability, digital integration, and market adaptation, driven by cleaner technologies, AI and big data usage, and product diversification. Innovations such as Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS), electrolysis-based production processes reducing emissions, and 3D...

